Psychological Adaptation / 06
Make sure to:
- Learn the definition of psychotic disorder, mood disorder and anxiety disorder.
- Identify the significant differences between psychotic disorder, mood disorder and anxiety disorder.
- Analyze the symptomatology of psychotic disorders, mood disorders and anxiety disorders.
 In the field of medicine, a challenging aspect is that there are many conditions that could present similar symptoms but are completely different illnesses. For example, both gastritis and an acute heart attack might present an oppressive and uncomfortable sensation on the chest. How worried should one be? What treatment is needed? These are questions that concern patients. And just like in more physical ailments, the same happens with mental illnesses.
In the field of medicine, a challenging aspect is that there are many conditions that could present similar symptoms but are completely different illnesses. For example, both gastritis and an acute heart attack might present an oppressive and uncomfortable sensation on the chest. How worried should one be? What treatment is needed? These are questions that concern patients. And just like in more physical ailments, the same happens with mental illnesses.
Nowadays, the term mental health defined by international organizations specialized in health issues (such as the WHO and PAHO) encompasses the absence of mental disorders or disabilities. This can be influenced by individual, social, family, school risk factors, among others. It is a known fact that everyone is at risk for developing a mental health condition regardless of age, sex, socioeconomic status or race. Despite this, studies have identified that one in every eight people in the world currently suffers from some mental disorder, representing approximately 970 million people under psychiatric treatment internationally.
Disorders such as anxiety and depression are among the most common mental health conditions that affect the general population (World Health Organization, 2022).
3.1 Psychotic Disorders
 Psychotic disorders are a set of serious mental illnesses that may appear during any stage of life. They are characterized by presenting symptoms such as mental disconnection or distortion of reality, and generating individual thoughts and perceptions different from those that other people have of their surroundings.
Psychotic disorders are a set of serious mental illnesses that may appear during any stage of life. They are characterized by presenting symptoms such as mental disconnection or distortion of reality, and generating individual thoughts and perceptions different from those that other people have of their surroundings.
The main alterations that characterize these disorders affect visual, olfactory, auditory and tactile perception. Also relevant is the appearance of emotional and behavioral difficulties that increase the stress and suffering of the patient and/or affected person, as well as the people close to them.
The characteristic and main disease of this group is schizophrenia. When the patient presents the symptoms, it is referred that they are in the middle of a psychotic episode or an outbreak.
The symptoms are usually divided into 2 large sections: positive psychotic symptoms and negative psychotic symptoms.
Table 1
Types of Psychotic Symptoms
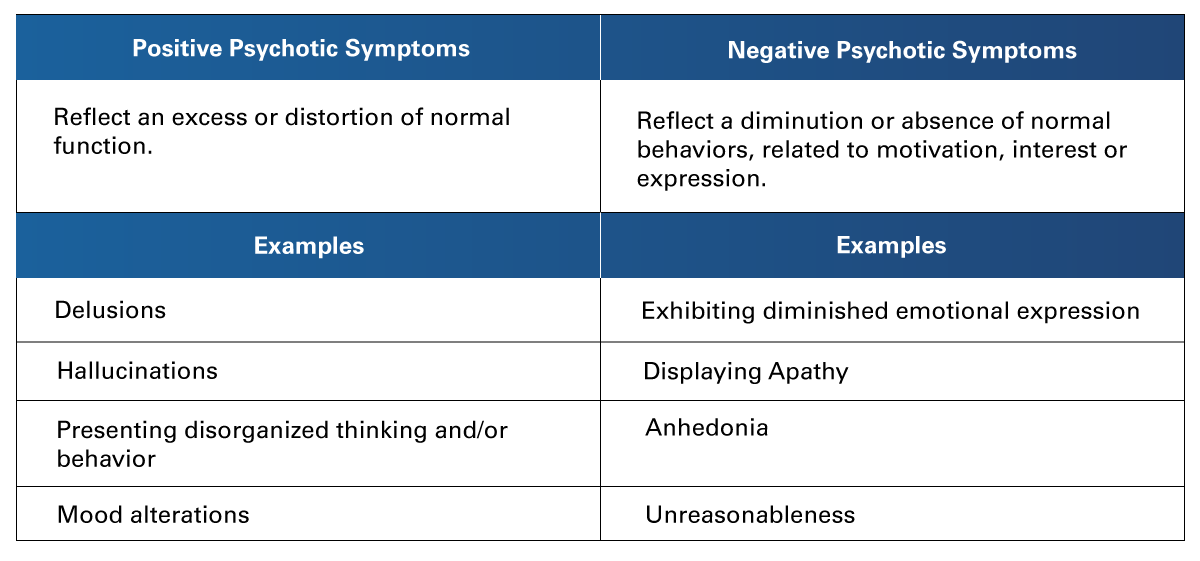 Adapted from Sant Joan de Deu Hospital. (2021). What are Psychotic Disorders? Symptoms and Types.
Adapted from Sant Joan de Deu Hospital. (2021). What are Psychotic Disorders? Symptoms and Types.
https://faros.hsjdbcn.org/es/articulo/trastornos-psicoticos-sintomas-tipos
As presented by the team at Sant Joan de Deu Hospital (2021), based on the characteristics and symptomatology of the psychotic disorders, the main types contemplated are:
- Delusional Disorder: characterized by delirium.
- Brief Psychotic Disorder: characterized by short-term (1 day to less than 1 month) positive psychotic symptoms.
- Schizophrenia: characterized by the appearance of at least 2 psychotic symptoms.
- Schizophreniform Disorder: symptoms similar to schizophrenia occur, but with a duration of less than 6 months.
3.2 Mood Disorders
 Unlike the previous disorders, in which the main characteristic is the alteration of reality, mood disorders are also known as affective or depressive disorders. As the name suggests, those affected by them have mood changes typically involving a period of high energy or euphoria and/or depression.
Unlike the previous disorders, in which the main characteristic is the alteration of reality, mood disorders are also known as affective or depressive disorders. As the name suggests, those affected by them have mood changes typically involving a period of high energy or euphoria and/or depression.
The most well-known mood disorder is depression. Studies estimate that globally 5% of adults suffer from it. It affects women more than men and is a mayor risk factor for suicide.
Depression (or depressive disorder) is said to be a common mental illness that is characterized by the loss of pleasure or interest in activities for prolonged periods of time. It leads to periodic mood changes, and it typically affects all life spheres, such as those of family, friends, relationships or work.
The primary symptoms include the sudden appearance of sadness, irritability, or loss of pleasure, accompanied by difficulty concentrating, guilt feelings, thoughts of death or suicide, sleep disturbances, changes in appetite, fatigue and changes in body weight and dietary regimen (World Health Organization, 2023).
Depressive episodes are usually classified according to their severity as mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the number and intensity of symptoms and the consequences on the patient's daily life.
Some other mood disorders such as bipolar disorder are characterized by unusual changes in the patient's mood. Also, seasonal affective disorder occurs due to the decrease or absence of daylight during autumn or winter. These also belong to the group of mood disorders (Medical News Today, 2021).
3.3 Anxiety Disorders
 In 2019, epidemiological studies report that 301 million people in the world suffered from an anxiety disorder, including 58 million children and adolescents. Anxiety disorders are characterized by anguish, fear and worry accompanied by behavioral disorders that lead to the patient’s functional disability. These disorders generate significant discomfort and affect the person's usual functioning regardless of their age, sex or social status. These disorders directly affect their social and individual relationships and daily activities (World Health Organization, 2022).
In 2019, epidemiological studies report that 301 million people in the world suffered from an anxiety disorder, including 58 million children and adolescents. Anxiety disorders are characterized by anguish, fear and worry accompanied by behavioral disorders that lead to the patient’s functional disability. These disorders generate significant discomfort and affect the person's usual functioning regardless of their age, sex or social status. These disorders directly affect their social and individual relationships and daily activities (World Health Organization, 2022).
Based on the characteristics of the symptoms and the triggers, the main types of anxiety disorders considered are:
Table 2
Type of Anxiety Disorders
 Adapted from Forcadell, E. (2019). What is Anxiety? Hospital Clinic Barcelona.
Adapted from Forcadell, E. (2019). What is Anxiety? Hospital Clinic Barcelona.
https://www.clinicbarcelona.org/asistencia/enfermedades/trastornos-de-ansiedad
It is important to consider that the same person can present several anxiety disorders at the same time, and it is not unusual for them to have other psychiatric disorders of various kinds such as mood, substance abuse, etc.
 Suffering from one or more mental disorders limits individuals to develop effectively in their biopsychosocial sphere. Unfortunately, every day there are more people who suffer from mental illnesses due to the various social conditions in which our daily lives develop. Social stressors like wars, economic devaluations, unemployment, migration, and poverty specifically negatively affect the mental health of the population. The national and international health systems have not adequately responded to the needs of people who suffer from mental disorders, and it is evident that these systems do not have the necessary resources to do so. That is why the prevalence of these conditions is and will be one of the main public health issues worldwide.
Suffering from one or more mental disorders limits individuals to develop effectively in their biopsychosocial sphere. Unfortunately, every day there are more people who suffer from mental illnesses due to the various social conditions in which our daily lives develop. Social stressors like wars, economic devaluations, unemployment, migration, and poverty specifically negatively affect the mental health of the population. The national and international health systems have not adequately responded to the needs of people who suffer from mental disorders, and it is evident that these systems do not have the necessary resources to do so. That is why the prevalence of these conditions is and will be one of the main public health issues worldwide.
- Forcadell, E. (2019, January 29). What is Anxiety? Hospital Clinic Barcelona. https://www.clinicbarcelona.org/asistencia/enfermedades/trastornos-de-ansiedad
- Miranda, S. (2021, August 20). Mental Health: Definition, Common Disorders, First Signs and More. Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/es/salud-mental
- Sant Joan de Deu. (2021, December 22). What are Psychotic Disorders? Symptoms and Types. https://faros.hsjdbcn.org/es/articulo/trastornos-psicoticos-sintomas-tipos
- World Health Organization. (2022, June 8). Mental disorders. https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-disorders
- World Health Organization. (2023, March 31). Depression. https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression
The following links do not belong to Tecmilenio University, when accessing to them, you must accept their terms and conditions.
Videos
- Psych2go. (2021, January 4). 5 Signs of a Psychotic Disorder [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/WWjpw51YWsE?si=sQyQjlZDVgyuPw9y
- Psych Hub. (2020, January 7). What is an Anxiety Disorder? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/vtUdHOx494E?si=C3J_uK_UX3p9oHJb
La obra presentada es propiedad de ENSEÑANZA E INVESTIGACIÓN SUPERIOR A.C. (UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO), protegida por la Ley Federal de Derecho de Autor; la alteración o deformación de una obra, así como su reproducción, exhibición o ejecución pública sin el consentimiento de su autor y titular de los derechos correspondientes es constitutivo de un delito tipificado en la Ley Federal de Derechos de Autor, así como en las Leyes Internacionales de Derecho de Autor.
El uso de imágenes, fragmentos de videos, fragmentos de eventos culturales, programas y demás material que sea objeto de protección de los derechos de autor, es exclusivamente para fines educativos e informativos, y cualquier uso distinto como el lucro, reproducción, edición o modificación, será perseguido y sancionado por UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO.
Queda prohibido copiar, reproducir, distribuir, publicar, transmitir, difundir, o en cualquier modo explotar cualquier parte de esta obra sin la autorización previa por escrito de UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO. Sin embargo, usted podrá bajar material a su computadora personal para uso exclusivamente personal o educacional y no comercial limitado a una copia por página. No se podrá remover o alterar de la copia ninguna leyenda de Derechos de Autor o la que manifieste la autoría del material.