Health Promotion and Maintenance / 09
Make sure to:
- Effectively utilize knowledge of pregnancy loss in clinical practice.
- Deliver care for pregnant clients experiencing placental disorders.
- Provide comprehensive nursing care to clients facing disorders during pregnancy, labor, and the post-partum period.
 Maternal complications can arise at any stage of pregnancy, labor, and the post-partum period. Nurses are responsible for assessing pregnant clients for any such complications and adapting their care plans to ensure a safe delivery. Additionally, the health and the well-being of pregnant clients must be continuously assessed during the post-partum period.
Maternal complications can arise at any stage of pregnancy, labor, and the post-partum period. Nurses are responsible for assessing pregnant clients for any such complications and adapting their care plans to ensure a safe delivery. Additionally, the health and the well-being of pregnant clients must be continuously assessed during the post-partum period.
In this learning experience, learners will gain insights into nursing considerations relevant to pregnancy loss, placental disorders, and various complications that may occur during pregnancy, labor, and the post-partum period.
3.1 Pregnancy Loss
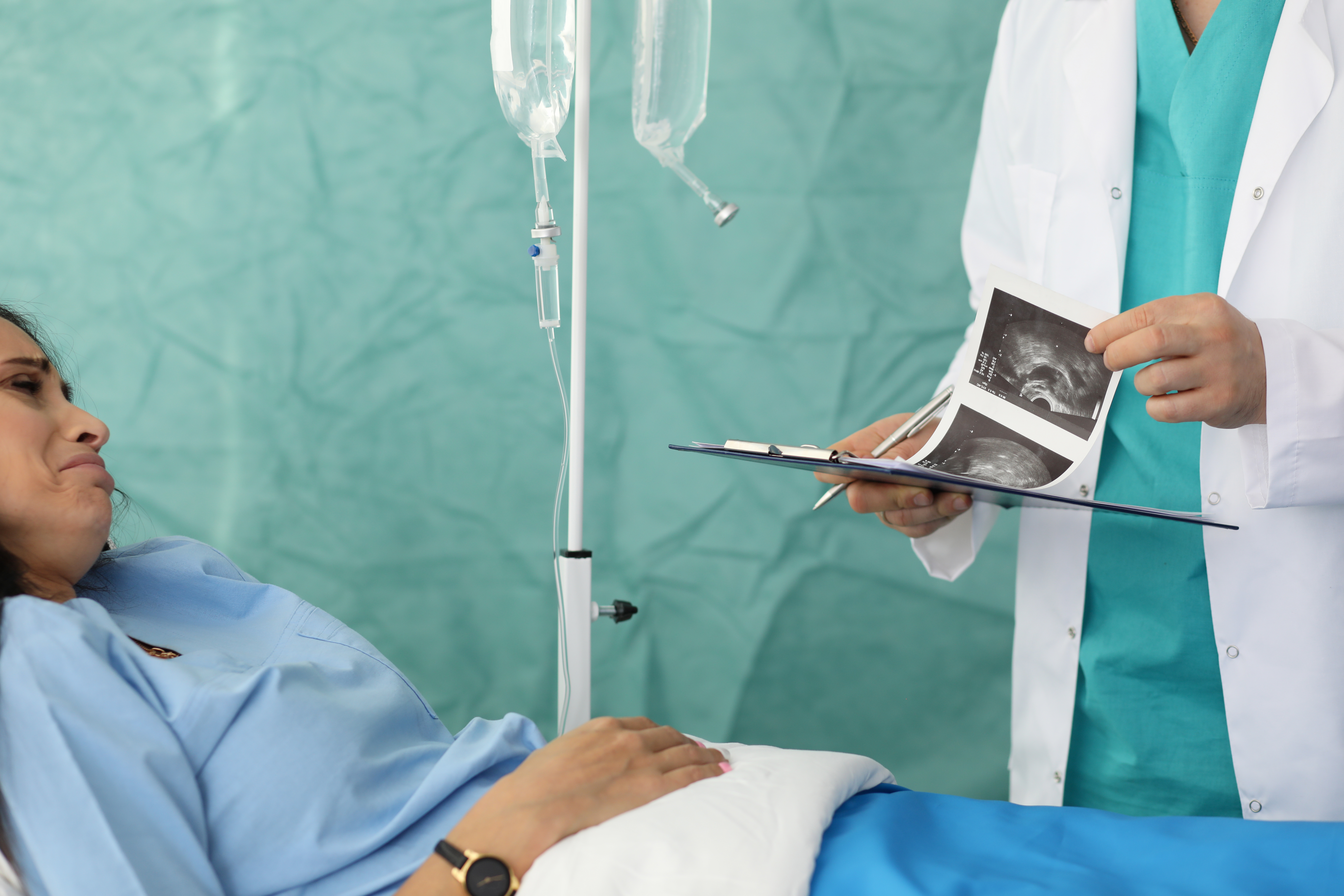 Nurses often support clients during pregnancy loss, which may result from an ectopic pregnancy or an abortion. Ectopic pregnancies occur when fertilized eggs implant outside the uterus (Burke, 2024). If the fetus continues to grow in these areas, such as the fallopian tube, serious complications like fallopian tube rupture and hemorrhage can arise. Early identification of ectopic pregnancy and subsequent surgical intervention can prevent rupture. Nurses must be vigilant in recognizing the warning signs of ectopic pregnancy, enabling them to promptly alert the client’s primary care provider and aid in management. These warning signs include abdominal pain, faintness, vomiting, nausea, and brown vaginal discharge (Burke, 2024).
Nurses often support clients during pregnancy loss, which may result from an ectopic pregnancy or an abortion. Ectopic pregnancies occur when fertilized eggs implant outside the uterus (Burke, 2024). If the fetus continues to grow in these areas, such as the fallopian tube, serious complications like fallopian tube rupture and hemorrhage can arise. Early identification of ectopic pregnancy and subsequent surgical intervention can prevent rupture. Nurses must be vigilant in recognizing the warning signs of ectopic pregnancy, enabling them to promptly alert the client’s primary care provider and aid in management. These warning signs include abdominal pain, faintness, vomiting, nausea, and brown vaginal discharge (Burke, 2024).
Both intentional and unintentional abortion can occur. In cases of intentional abortion, the pregnant client actively seeks medical assistance to terminate their pregnancy. Conversely, some clients experience spontaneous pregnancy loss. This type of loss, also known as miscarriage or unintended abortion, often happens during the first trimester (Burke, 2024). Clients who have uterine abnormalities, thyroid disorders, infections, diabetes, or exposure to radiation and/or chemicals face a higher risk of spontaneous abortion. These cases may involve inevitable or threatened spontaneous abortion, or complete and incomplete abortion (Burke, 2024).
Table 1
Types of Spontaneous Abortion and Their Signs and Symptoms
 Adapted from Burke, A. (2024). Anti/Intra/Postpartum and Newborn Care: NCLEX-RN. https://www.registerednursing.org/nclex/anti-intra-postpartum-newborn-care/#conception
Adapted from Burke, A. (2024). Anti/Intra/Postpartum and Newborn Care: NCLEX-RN. https://www.registerednursing.org/nclex/anti-intra-postpartum-newborn-care/#conception
According to Burke (2024) some key considerations for healthcare providers when caring for clients experiencing a spontaneous abortion include:
- Assisting with ultrasound and speculum vaginal examinations, which are essential for diagnosing spontaneous abortion.
- Preparing the client for, and assisting with, dilation and curettage to remove any remaining pregnancy tissue from the uterus.
- Administering misoprostol as prescribed to expel remaining pregnancy products.
- Administering intravenous fluid or blood or blood products as ordered, where necessary.
- Monitoring the client for complications such as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
Furthermore, it is crucial for nurses to comply with their healthcare facility’s policies and procedures regarding pregnancy loss. Additionally, nurses should:
- Assess clients for any negative emotional responses.
- Report severe negative emotions to the clients’ healthcare providers.
- Provide emotional support and resources to clients who are experiencing negative emotions.
3.2 Disorders of the Placenta
 It is essential for nurses to actively participate as members of the healthcare team in assessing and managing pregnant clients with placental disorders. The primary goals include ensuring the safe delivery of the baby and preventing severe maternal complications. Such placental disorders include placenta previa and abruptio placentae (premature separation of the placenta).
It is essential for nurses to actively participate as members of the healthcare team in assessing and managing pregnant clients with placental disorders. The primary goals include ensuring the safe delivery of the baby and preventing severe maternal complications. Such placental disorders include placenta previa and abruptio placentae (premature separation of the placenta).
Placenta Previa
During placenta previa, the pregnant client experiences vaginal bleeding because the placenta implants in the lower segment of the uterus (Kaplan Nursing, 2023). It may position itself close to, or completely over, the cervix opening (Kaplan Nursing, 2023). This condition can jeopardize fetal gas exchange and fluid volume.
According to Kaplan Nursing (2023), nursing considerations for clients with placenta previa, both during hospitalization and at home, include:
During Hospitalization:
- Providing support to clients who may feel anxious and fearful.
- Following and assisting with the healthcare provider’s orders.
- Enforcing bed rest, maintaining either the Trendelenburg or the side-lying position for at least 3 days.
- Conducting an ultrasound to determine the exact location of the placenta.
- Avoiding vaginal and rectal examination.
- Performing amniocentesis to determine fetal status, including lung maturity and bleeding.
- Monitoring the extent of bleeding by weighing peri-pads and assessing hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.
At-Home Instructions:
- Limit physical activities.
- Avoid sexual activity, douching, or using enemas.
- Schedule a non-stress test at least once every week or every two weeks.
Clients with significant bleeding, those in labor, or experiencing other complications will undergo a cesarean section. In such cases, nurses should prepare the client for the procedure and aid during and after the surgery.
Abruptio Placentae
Abruptio placentae should be considered in pregnant clients who experience either minimal or excessive painful dark red vaginal bleeding (Kaplan Nursing, 2023). These clients may report abdominal pain and exhibit tenderness in the lower abdomen, over the uterus. Along with fetal distress, the client may present with shock or experience contractions. This condition is more prevalent in clients with maternal hypertension and those who use cocaine (Kaplan Nursing, 2023).
It is important for nurses to:
- Observe the client for signs of shock.
- Monitor the client for fetal distress.
- Assist with preparation for prompt delivery.
- Watch for complications during the post-partum period, including:
- Infection.
- Pulmonary embolism.
- Renal failure.
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
- Additionally, nurses should evaluate:
- The client’s fluid and electrolyte balance.
- The effectiveness of measures taken to prevent complications.
3.3 Disorders during Pregnancy, Labor, and Post-Partum
 Disorders during pregnancy, labor, and the post-partum period pose risks to the well-being of pregnant clients, their unborn child, and/or their newborn.
Disorders during pregnancy, labor, and the post-partum period pose risks to the well-being of pregnant clients, their unborn child, and/or their newborn.
Disorders During Pregnancy
According to Burke (2024) and Kaplan Nursing (2023), nurses are responsible for assessing pregnant clients and implementing the order of healthcare providers for disorders that may occur during pregnancy. These disorders include:
- Cardiac disease.
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC).
- Diabetes.
- Hypertension.
- Pre-eclampsia.
- Eclampsia.
- Sexually transmitted infections:
- Gonorrhea.
- Chlamydia.
- HIV/AIDS.
- Other Infections:
- Salpingitis.
- Endometritis.
- Tubo-ovarian abscesses.
- Candida albicans.
- Chorioamnionitis.
Disorders During Labor
Nurses collaborate with healthcare providers to support their clients experiencing labor disorders or abnormalities that pose risks to the life of the clients and/or her unborn child. A cesarean birth is usually performed to ensure the well-being of both the client and fetus (Kaplan Nursing, 2023). According to Kaplan Nursing (2023), these disorders/abnormalities include:
- Maternal Factors:
- Abnormal or difficult labor, also known as dystocia.
- Hypertensive states during pregnancy.
- Placenta previa or abruptio placentae.
- Fetal Factors:
- Fetal distress.
- Umbilical cord prolapse.
- Anomalies, such as hydrocephaly.
- Breech presentation.
Post-Partum Disorders
Post-partum disorders most commonly involve issues related to infection and bleeding (Burke, 2024). Suspect a local infection if the client exhibits redness, heat, swelling, and/or pain. Systemic infection indications include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, chills, fatigue, hyperthermia, prodromal malaise, tachypnea, tachycardia, anorexia, confusion, incontinence, and/or abdominal cramping. Therefore, nurses should conduct thorough post-partum assessments, encapsulated in the BUBBLE acronym (Burke, 2024).
- B for Breasts: Breasts may become engorged, especially in clients who are breastfeeding.
- U for Uterine Fundus: Assess the placement, consistency, and height of the uterine fundus.
- The first B for Bowel: Includes assessing the gastrointestinal tract functions.
- The second B for Bladder Function: Anticipate reduced urine output during the first one to two days post-partum.
- L for Lochia: Evaluate the color, consistency, amount, and odor.
- E for Episiotomy: Check for swelling (edema) and redness in clients who have undergone an episiotomy.
Post-Partum Hemorrhage
Post-partum hemorrhages defined as blood loss exceeding 500 mL after vaginal delivery or 1000 mL following a cesarean section (Kaplan Nursing, 2023). Nurses should assess the uterine fundus and measure vaginal bleeding by weighing sanitary napkins (peri-pads). Clients with a history of multiple pregnancies, retained placenta fragments, a distended uterus, prolonged labor, or the delivery of a large infant are at a higher risk for post-partum hemorrhage and require closer monitoring. (Kaplan Nursing, 2023). Uterine massage can help prevent hemorrhage. Nurses should administer medications like oxytocin, prostaglandin, misoprostol, or methylergonovine as prescribed in the event of post-partum hemorrhage.
It is also important for nurses to assist with diagnostic tests, such as cultures (lochia, urine, and blood) and white blood cell counts (Kaplan Nursing, 2023). Additionally, clients should be encouraged to consume balanced meals and adequate fluids, get sufficient sleep, ambulate as soon as possible, and change their sanitary pads frequently. Antibiotics should be administered as prescribed (Kaplan Nursing, 2023).
Post-Partum Depression
Post-partum depression can develop within one month to one year after childbirth (Kaplan Nursing, 2023). It is characterized by symptoms such as crying, sadness, concentration problems, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and changes in appetite. It is important for nurses to carefully observe clients for these signs. The nursing evaluation should assess the client’s ability to cope with the stress of caring for a newborn and the capacity to express her feelings. Nursing care plans should include referral to support groups and mental health professionals like psychiatrists, assistance with baby care, administration of prescribed medication, and assessment for suicide (Kaplan Nursing, 2023).
 To conclude, the learner has gained knowledge regarding the identification and management of maternal complications.
To conclude, the learner has gained knowledge regarding the identification and management of maternal complications.
The provided resources will increase proficiency in maternal complications in clinical practice. The goals are to facilitate success on the NCLEX examination and in the workplace.
After reviewing the resources, identify these specific areas for improvement and concentrate on them.
- Burke, A. (2024, January 20). Anti/Intra/post-partum and Newborn Care: NCLEX-RN. https://www.registerednursing.org/nclex/anti-intra-postpartum-newborn-care/#conception
- Kaplan Nursing. (2023). NCLEX-RN Content Review Guide: Preparation for the NCLEX-RN Examination (9th ed.). Kaplan Test Prep.
The following links do not belong to Tecmilenio University, when accessing to them, you must accept their terms and conditions.
Reading
- Cleveland Clinic. (2022, November 14). Pregnancy Complications. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/24442-pregnancy-complications
Video
- Family Health Centers of San Diego. (2021, February 22). Most Common Pregnancy Complications to Watch out For [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/2l9_WPsKRkg
La obra presentada es propiedad de ENSEÑANZA E INVESTIGACIÓN SUPERIOR A.C. (UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO), protegida por la Ley Federal de Derecho de Autor; la alteración o deformación de una obra, así como su reproducción, exhibición o ejecución pública sin el consentimiento de su autor y titular de los derechos correspondientes es constitutivo de un delito tipificado en la Ley Federal de Derechos de Autor, así como en las Leyes Internacionales de Derecho de Autor.
El uso de imágenes, fragmentos de videos, fragmentos de eventos culturales, programas y demás material que sea objeto de protección de los derechos de autor, es exclusivamente para fines educativos e informativos, y cualquier uso distinto como el lucro, reproducción, edición o modificación, será perseguido y sancionado por UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO.
Queda prohibido copiar, reproducir, distribuir, publicar, transmitir, difundir, o en cualquier modo explotar cualquier parte de esta obra sin la autorización previa por escrito de UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO. Sin embargo, usted podrá bajar material a su computadora personal para uso exclusivamente personal o educacional y no comercial limitado a una copia por página. No se podrá remover o alterar de la copia ninguna leyenda de Derechos de Autor o la que manifieste la autoría del material.