Reduction of Risk Potencial / 05
Make sure to:
- Define the measures by which the patient is identified.
- Identify all moments for patient identity verification.
- Summarizes data that should not be used as identifiers.
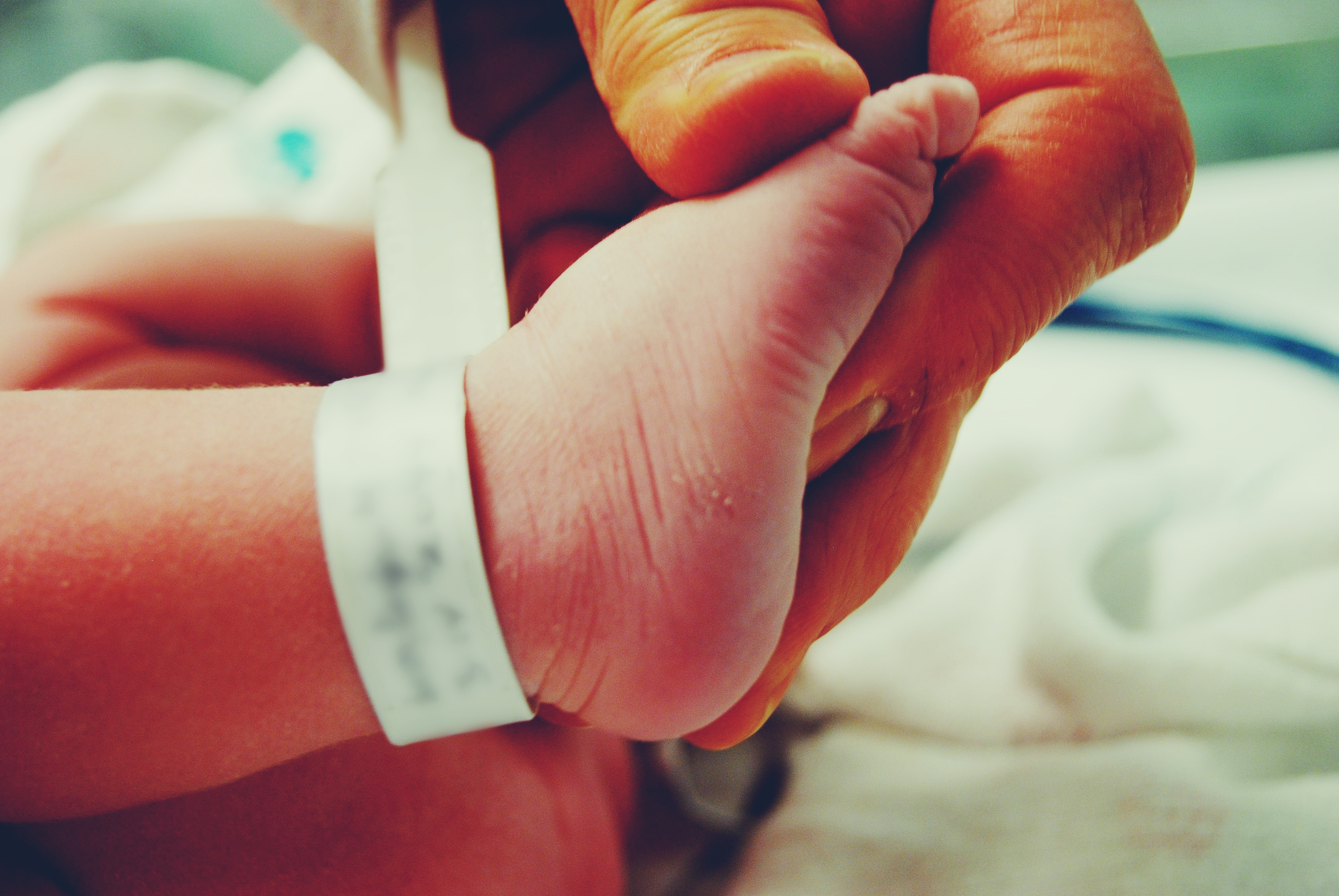 According to Panattieri et al. (2019), "Humans are fallible and errors are to be expected, even in the best organizations". However, over time, strategies have been implemented to function as patient safety barriers.
According to Panattieri et al. (2019), "Humans are fallible and errors are to be expected, even in the best organizations". However, over time, strategies have been implemented to function as patient safety barriers.
One such strategy is the accurate identification of the patient and its application prevents, for example, performing procedures on a patient that do not correspond to them or reporting results of laboratory or cabinet tests from another patient.
The application of safety measures and their verification before performing procedures ensures the safety of processes for the patient.
1.1 Background and Importance
 Patient safety encompasses the practices and actions undertaken by healthcare institutions to reduce and eliminate the risks of avoidable harm related to healthcare. Table 1 summarizes these strategies starting with the so-called Essential Patient Safety Actions.
Patient safety encompasses the practices and actions undertaken by healthcare institutions to reduce and eliminate the risks of avoidable harm related to healthcare. Table 1 summarizes these strategies starting with the so-called Essential Patient Safety Actions.
However, the responsibility for implementation is not solely that of healthcare institutions; it also extends to the awareness of healthcare personnel. Participation in risk management implies a state of continuous alertness for the detection of situations that endanger patient safety, enabling proactive intervention before avoidable harm occurs.
Despite having these strategies in place, the World Health Organization (2023) still states that "some common adverse events that can cause preventable harm are due to errors made during patient identification, diagnosis, or medication prescription, as well as patient falls, unscreened blood transfusions, and preventable risks during surgical procedures".
Patient care starts with reliable identification, ensuring that the individual is the intended person for the service or treatment; and then and subsequently matching the service or treatment to that individual. Errors can occur through a) misidentification of the patient, b) misidentification of body parts, and c) incorrect use of biological materials (specimens or anatomical parts) from the wrong patient (De Rezende et al., 2019).
Table 1
Reduction of Risk Potential
 Adapted from Secretaría de Salud. (2023). Acciones Esenciales para la Seguridad del Paciente. http://csg.gob.mx/descargas/pdf/certificacion-establecimientos/modelo_de_seguridad/acciones_ModeloCSG/AESPCSG-DGCES16junio2023.pdf
Adapted from Secretaría de Salud. (2023). Acciones Esenciales para la Seguridad del Paciente. http://csg.gob.mx/descargas/pdf/certificacion-establecimientos/modelo_de_seguridad/acciones_ModeloCSG/AESPCSG-DGCES16junio2023.pdf
1.2 Labeling Patient Information (Name and Date of Birth)
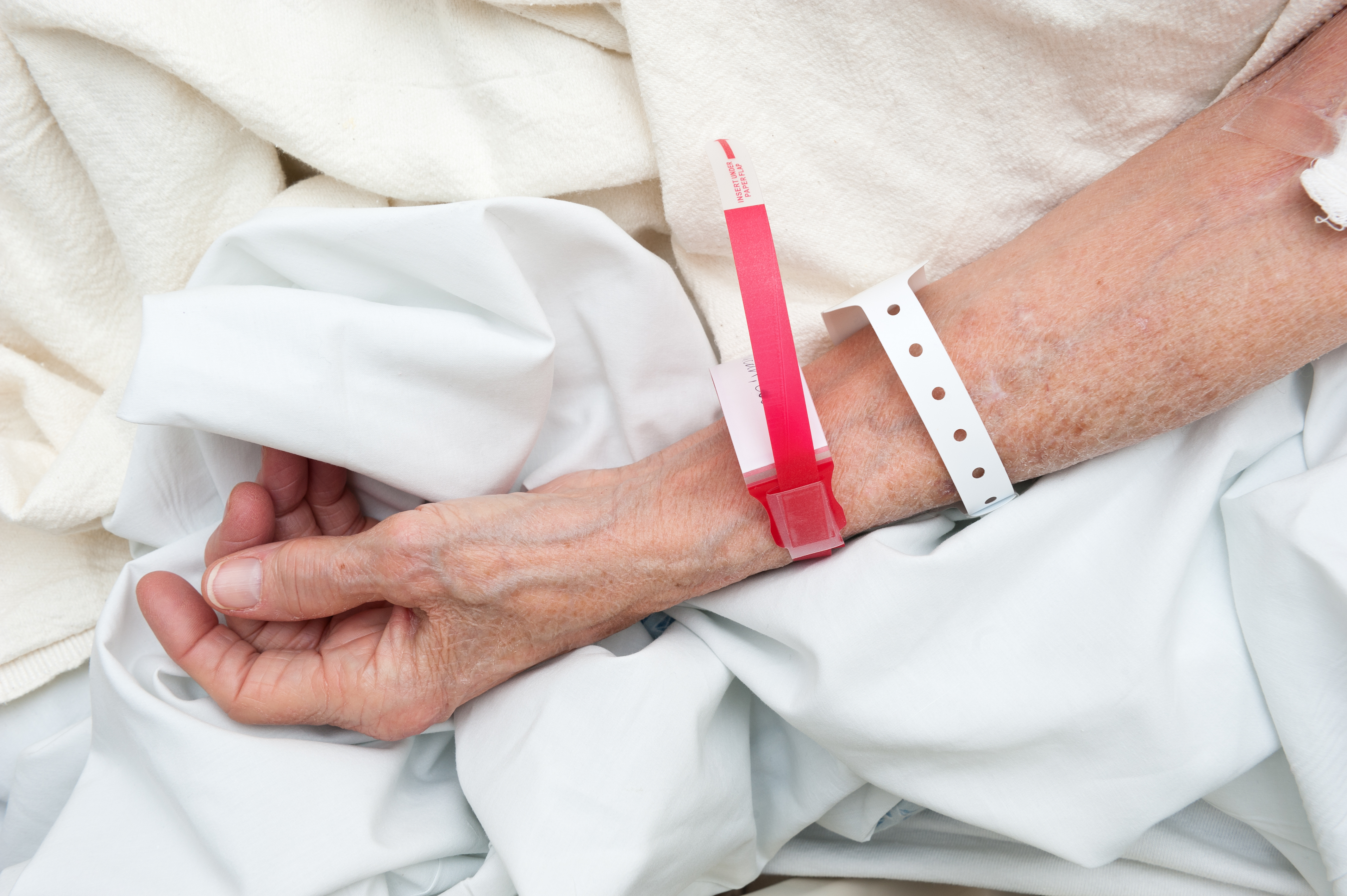 Each institution establishes its own process for patient identification. However, this alone is insufficient; the nursing staff must recognize that before conducting any procedure, the patient's identity must be verified, as errors can occur at any point during the patient's care.
Each institution establishes its own process for patient identification. However, this alone is insufficient; the nursing staff must recognize that before conducting any procedure, the patient's identity must be verified, as errors can occur at any point during the patient's care.
Certain circumstances may contribute to these errors. The patient may experience alterations in consciousness due to the effects of sedatives or unconsciousness, confusion, disorientation, or sensory problems such as hypoacusis. Additionally, patients may face challenges in communication, such as a lack of knowledge of the language, or might be a minor.
Errors can also arise when the patient's identity is not confirmed, and only the bed or stretcher number is considered. In such situations, the patient may have changed beds, and another patient may already occupy the bed, or the identification card of the previous patient may not have been removed from the bedside. Relying solely on the patient's diagnosis or the specialty attending to the patient is not advisable, as this factor can also change.
To reliably identify the individual for whom the service, procedure or treatment is intended and ensure alignment with the correct person, it has been established that at least two pieces of information must be included on the bracelet: the patient's name and date of birth (Secretaría de Salud, 2023).

Before any procedure is undertaken, these details should be cross verified with the patient's identification bracelet, which should contain identical information. Therefore, before proceeding with the procedure, the patient/caregiver is requested to provide their full name and date of birth and/or medical history or document number (when possible/practical).
Table 2 illustrates the crucial moments during which patient identification should occur before initiation.

Table 2
Critical Moments: Patient Identification Prior to Initiation
 Adapted from Secretaría de Salud. (2023). Acciones Esenciales para la Seguridad del Paciente. http://csg.gob.mx/descargas/pdf/certificacion-establecimientos/modelo_de_seguridad/acciones_ModeloCSG/AESPCSG-DGCES16junio2023.pdf
Adapted from Secretaría de Salud. (2023). Acciones Esenciales para la Seguridad del Paciente. http://csg.gob.mx/descargas/pdf/certificacion-establecimientos/modelo_de_seguridad/acciones_ModeloCSG/AESPCSG-DGCES16junio2023.pdf
It is important to note that issues may arise with the use of bracelets, as the lettering can become illegible, they may come off the wrist, especially in children or babies, or they may break. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor their condition, and if necessary, replace them.
1.3 Patient and Family Participation
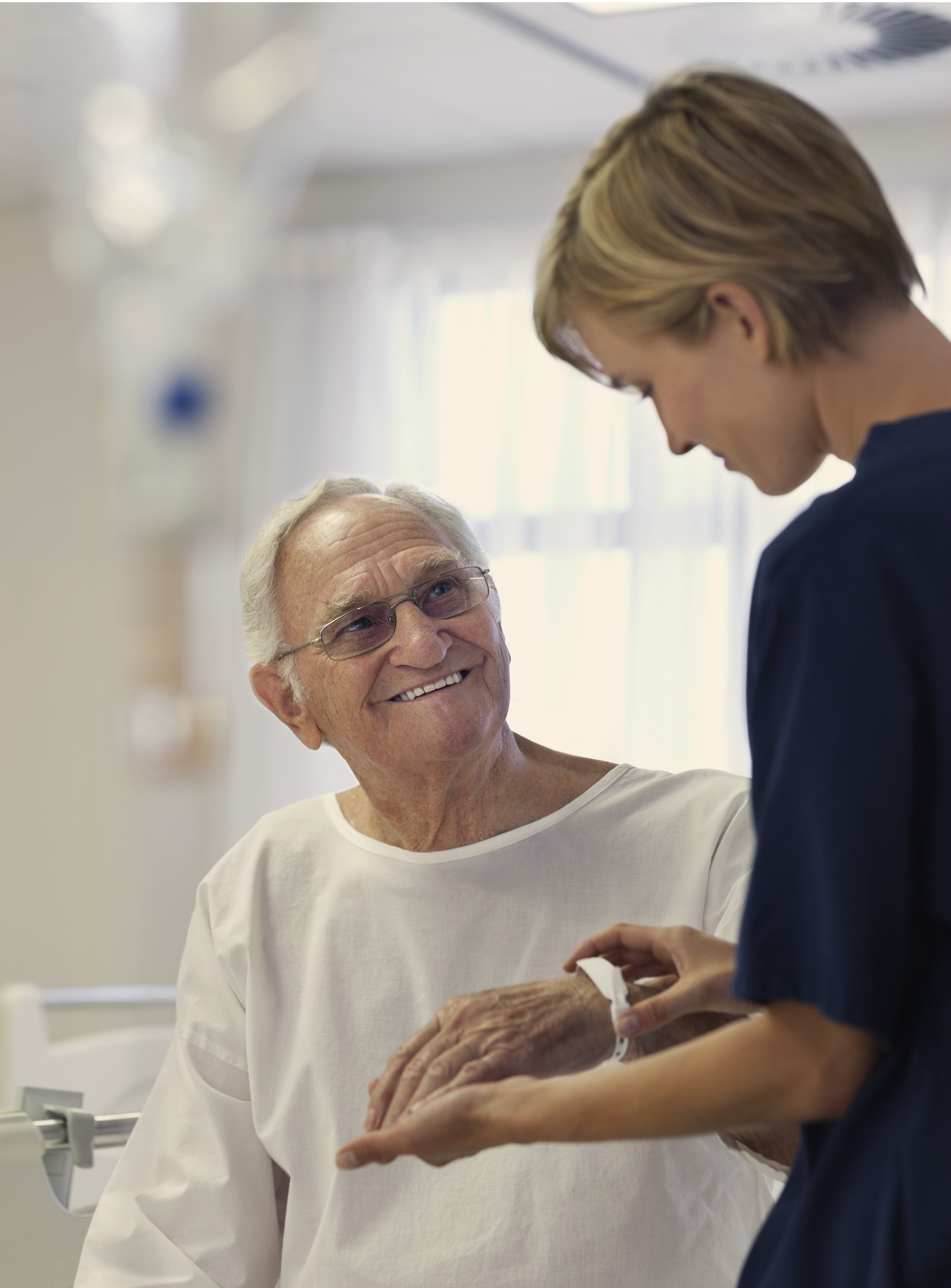 As long as the patient is capable, they can provide the necessary information for the documents in their file and for their identification, either on the bracelet, the identification card, or any other document required during their care.
As long as the patient is capable, they can provide the necessary information for the documents in their file and for their identification, either on the bracelet, the identification card, or any other document required during their care.
Involvement of family or caregivers in maintaining this safety barrier is crucial. They provide or verify identification data, especially when the patient is unable to do so. They are sensitized to and understand the importance of the patient wearing the bracelet at all times during hospitalization.
There is a risk that the bracelet may lose its utility due to breakage, coming off the wrist, getting lost, especially in small children or very thin individuals, or becoming illegible due to humidity. These situations necessitate constant monitoring, where the family member can assist in keeping watch so that, if something happens to the bracelet, it can be promptly replaced.
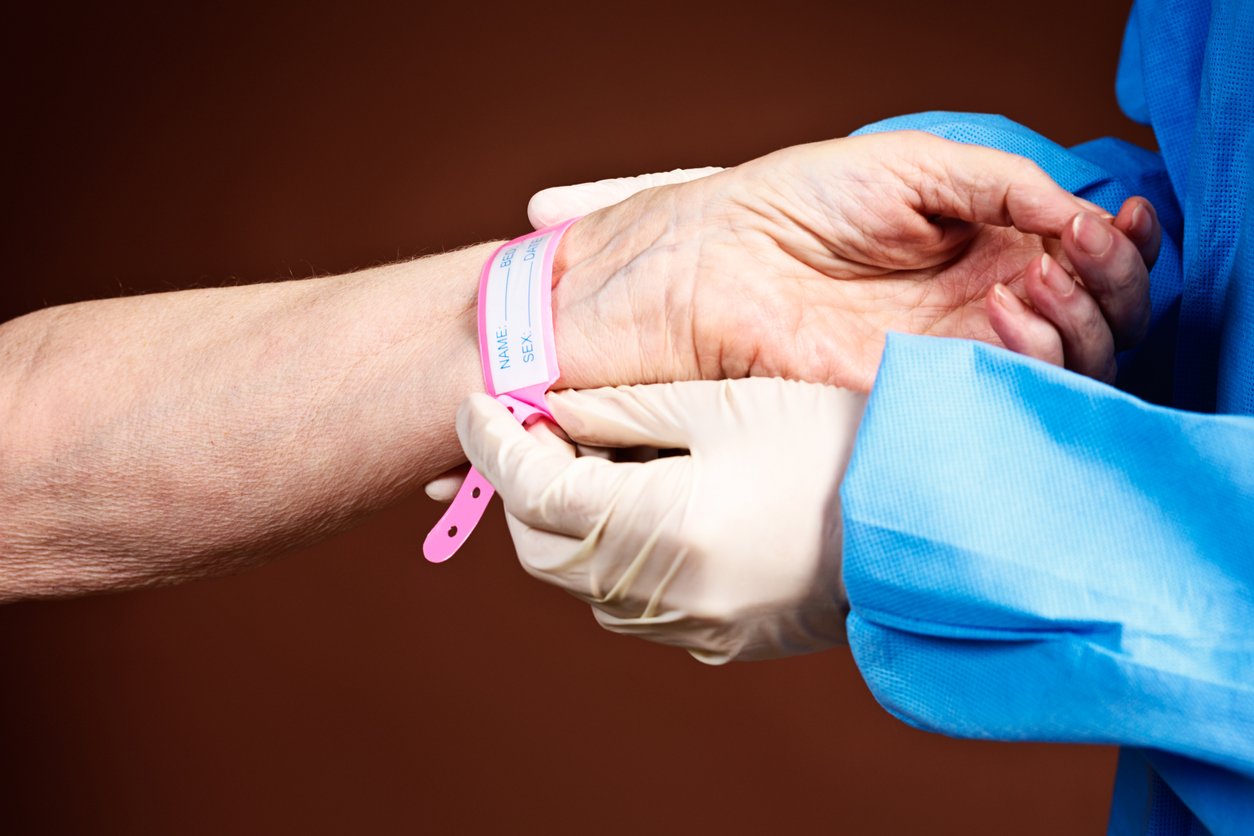 By the end of this learning experience, the learner will understand the significance of correctly identifying and verifying the patient's data before performing a procedure, thereby implementing a primary safety measure for the patient. Errors resulting from the patient misidentification can range in severity, from the administration of a drug that was not intended to more critical issues such as the omission of a surgical or invasive procedure or one for another patient.
By the end of this learning experience, the learner will understand the significance of correctly identifying and verifying the patient's data before performing a procedure, thereby implementing a primary safety measure for the patient. Errors resulting from the patient misidentification can range in severity, from the administration of a drug that was not intended to more critical issues such as the omission of a surgical or invasive procedure or one for another patient.
This barrier is particularly established from admission and persists throughout each process involving the patient during their hospital stay. Nursing plays a vital role in every stage, underscoring the necessity of continuous monitoring that nursing can provide for the patient’s benefit.
Furthermore, the comprehensive explanation emphasizes why the full name and date of birth serve as the optimal choices for patient identification, moving away from less secure practices like using bed number or the patient's diagnosis. Through these actions, nursing guarantees quality and safe care for the patient at every level of care, ultimately contributing to success in passing the NCLEX exam.
- De Rezende, H. A., Melleiro, M. M., & Shimoda, G. T. (2019). Interventions to Reduce Patient Identification Errors in the Hospital Setting: A Systematic Review Protocol. JBI Evidence Synthesis, 17(1), 37-42. https://doi.org/10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003895
- Panattieri, N. D., Dackiewicz, N., Arpí, L., Godio, C., Andión, E., Negrette, C., Sabio Paz, V., Nieto, R., & Jorro, F. (2019). Consenso: Seguridad del paciente y las metas internacionales. Archivos Argentinos de Pediatria, 117(6), S277-S309. https://doi.org/10.5546/aap.2019.s277
- Secretaría de Salud. (2023). Acciones Esenciales para la Seguridad del Paciente. http://csg.gob.mx/descargas/pdf/certificacion-establecimientos/modelo_de_seguridad/acciones_ModeloCSG/AESPCSG-DGCES16junio2023.pdf
- World Health Organization. (2023, September 11). Patient Safety. https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/patient-safety
The following links do not belong to Tecmilenio University, when accessing to them, you must accept their terms and conditions.
Readings
- World Health Organization. (n.d.). Draft Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021–2030. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/patient-safety/gpsap/final-draft-global-patient-safety-action-plan-2021-2030.pdf?sfvrsn=fc8252c5
Videos
- Hani Hassan. (2020, April 21). International Patient Safety Goals [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p8EL6FP8W0Q
La obra presentada es propiedad de ENSEÑANZA E INVESTIGACIÓN SUPERIOR A.C. (UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO), protegida por la Ley Federal de Derecho de Autor; la alteración o deformación de una obra, así como su reproducción, exhibición o ejecución pública sin el consentimiento de su autor y titular de los derechos correspondientes es constitutivo de un delito tipificado en la Ley Federal de Derechos de Autor, así como en las Leyes Internacionales de Derecho de Autor.
El uso de imágenes, fragmentos de videos, fragmentos de eventos culturales, programas y demás material que sea objeto de protección de los derechos de autor, es exclusivamente para fines educativos e informativos, y cualquier uso distinto como el lucro, reproducción, edición o modificación, será perseguido y sancionado por UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO.
Queda prohibido copiar, reproducir, distribuir, publicar, transmitir, difundir, o en cualquier modo explotar cualquier parte de esta obra sin la autorización previa por escrito de UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO. Sin embargo, usted podrá bajar material a su computadora personal para uso exclusivamente personal o educacional y no comercial limitado a una copia por página. No se podrá remover o alterar de la copia ninguna leyenda de Derechos de Autor o la que manifieste la autoría del material.