Medical Terminology / 02
Make sure to:
- Recognize medical terminology.
- Associate suffixes and prefixes to previous knowledge of medical terms.
- Review common healthcare terms.
- Interpret common healthcare terms in NCLEX style questions.
 Have you ever been to a foreign country for the first time? The biggest fear would be getting lost and not knowing how to get back to your hotel. During this time, the value of the GPS (Global Positioning System) becomes invaluable. Most of us have GPS on our mobile phones or smart devices, making moving around while we travel much easier.
Have you ever been to a foreign country for the first time? The biggest fear would be getting lost and not knowing how to get back to your hotel. During this time, the value of the GPS (Global Positioning System) becomes invaluable. Most of us have GPS on our mobile phones or smart devices, making moving around while we travel much easier.
Likewise, navigating the complexities of the human body is like exploring a foreign country, and just as a GPS helps us decipher the unfamiliar streets and landmarks, medical terminology acts as our guidebook, providing essential insight and directions through the intricate systems and functions.
Surely, if you are ill or have any medical condition, you would want people navigating your body to always arrive at the correct place on time and knowing what they are doing. Medical terminology is the GPS that guides doctors, nurses, and clinicians in moving across, side to side, in and out of the human body. Above all, safely moving or intervening to achieve the best medical outcome and navigate the patient's body with an assurance of understanding medical terminology gives you a sense of accomplishment (Singh, 2016).
1.1 Introduction to Medical Terminology
 The story of medical terminology begins with the ancient civilizations of Egypt, Greece, and Rome, where early medical practitioners laid the foundation for medical language (UHEROVá & Horňáková, 2013).
The story of medical terminology begins with the ancient civilizations of Egypt, Greece, and Rome, where early medical practitioners laid the foundation for medical language (UHEROVá & Horňáková, 2013).
During the great rule of Rome, which spanned several centuries, the field of medicine experienced significant development, and the medical language and terms underwent a profound influence from Latin scientific terms. This influence is attributed to the Roman Empire's adoption of Latin as the language of medicine, which continued to shape medical terminology for centuries to come.
The Renaissance period, known for its revival of arts, culture, and learning, also played a pivotal role in the evolution of medical terminology. Medical scholars during the Renaissance era recognized the value of classical languages, particularly Greek and Latin, in the study of medicine. As a result, a substantial portion of medical terminology during this period was believed to have up to 90% of its characteristics derived from these languages (Daly et al., 2005; Pepper, n.d.).
To develop a standardized and systematic vocabulary that could effectively express the complexity of human anatomy, diseases, and medical operations, Greek and Latin roots, prefixes, and suffixes were purposefully incorporated into medical nomenclature. Using this method, medical professionals from various geographic and linguistic backgrounds were able to communicate clearly and efficiently, overcoming language barriers and promoting the interchange of medical information. (Jóskowska & Grabarczyk, 2013).
The utilization of Latin and Greek in medical terminology also enabled medical professionals to pay homage to the historical contributions of ancient civilizations like Greece and Rome to the field of medicine. Many medical terms still in use today, such as "cardiology," "dermatology," and "neurology," can be traced back to their Greek and Latin origins (Jóskowska & Grabarczyk, 2013).
1.2 Prefixes and Suffixes
Mastering medical terminology is a comprehensive process that involves studying various aspects, with word roots being a fundamental component. Word roots constitute the core of a medical term, providing its essential meaning. By delving into the origins of these roots and their linguistic sources, learners who possess a strong grasp of Latin or Greek, like Spanish speakers, have a distinct advantage (i.e., un paso adelante).
In essence, understanding word roots enables students to decipher and remember complex medical terms more efficiently. Those with knowledge of Latin or Greek benefit from recognizing familiar elements that form the basis of numerous medical terms. For example, Spanish speakers can recognize that "paso" means "step," and "adelante" means "forward," allowing them to readily understand the concept of a "step ahead."
Word root can be modified using prefixes and suffixes to form new words with similar meanings. To understanding complex medical terms and developing a strong medical vocabulary, understanding root words is crucial.
For instance, in Greek, the word root lith signifies “stone” or “rock”. In a health report, the term “lithiasis” (Singh, 2016) indicates the presence of calcium stones in a patient. Now, here is an intriguing question: when you hear "lithiasis," do you envision a stone or perhaps think of lithium? Fear not, as “lithiasis” indeed refers to a stone formation. For Spanish speakers, it might even evoke the word “piedras”. Stone formations can occur in various places within the body. For instance, combining “gastro” (stomach) with “lith” (stone) gastroliths. And when we need to convey the removal of gall stones, we use the word "cholecystectomy," which breaks down into "chole" (bile), "cyst" (sac), and "ectomy" (removal).
In medical terminology, vowels called combining vowel (e.g., a, e, i, o, u)are often inserted between word roots to facilitate pronunciation. Among them, “o” is widely used, as seen in “Cardi/o”, “gastr/o”, and “oste/o”, all combining forms. However, other vowels like "e" can also serve this purpose.
Understanding word roots and their meanings unlocks a wealth of knowledge in medical terminology. By breaking down complex terms, we gain insights into medical conditions and procedures, enhancing our ability to communicate precisely and effectively in the ever-evolving world of healthcare.

The word root, also known as the combining form, serves to explicitly identify the body component that the term either depicts or is associated with. This distinction effectively eliminates many potential interpretations, allowing for a more concentrated analysis of a particular collection of biological data. These two lengthy enumerations of crucial roots, which may appear after any prefix or in front of any suffix, are presented in this section. These roots are systematically divided into two groups: inner root words, which describe the internal domain, and exterior root words, which describe aspects linked to the external surface of the body (Henderson & Dorsey, 2019).
Table 1
Exterior Root Words and their Meaning (from A to I)
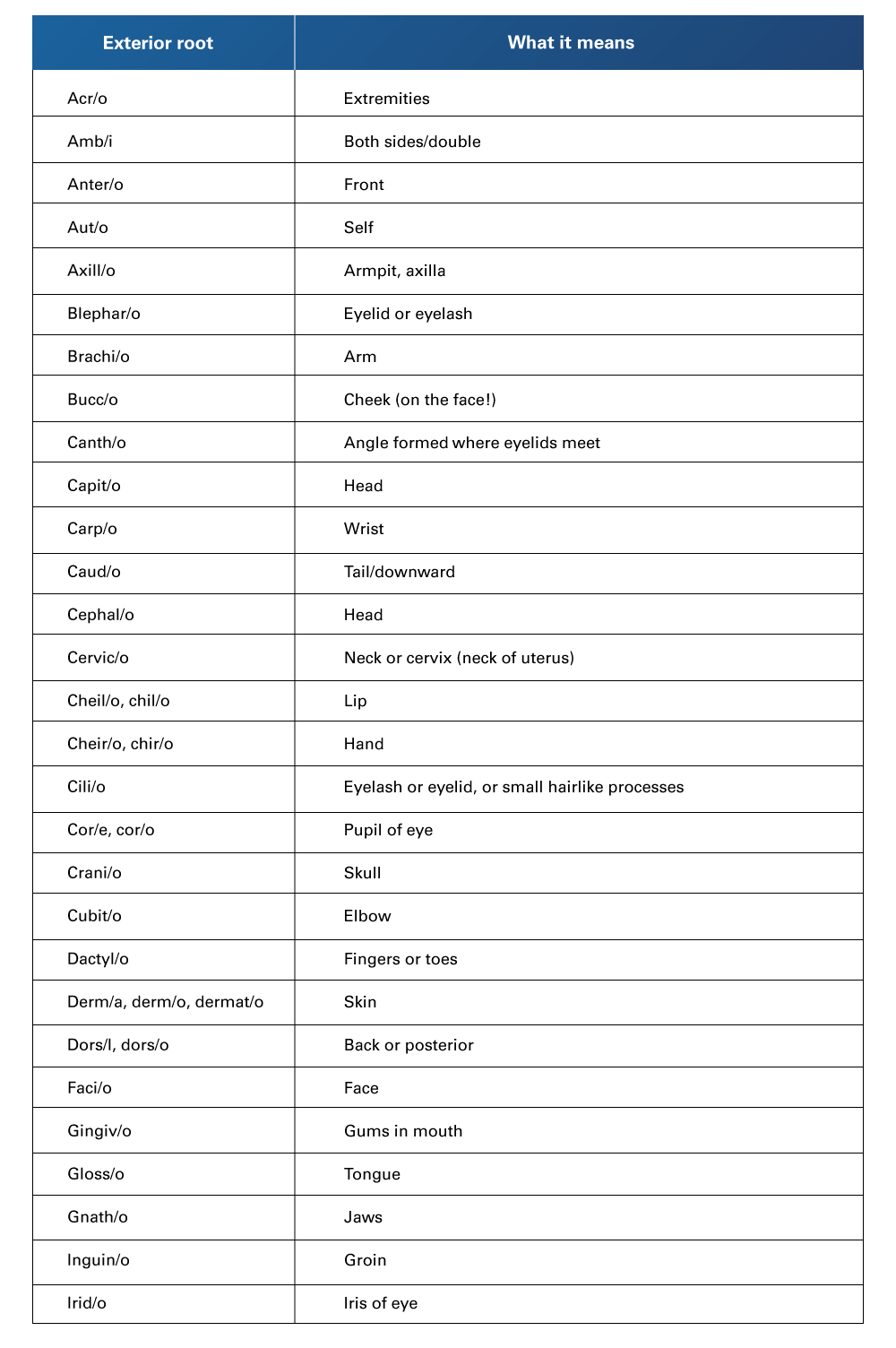 Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Table 2
Exterior Root Words and their Meaning (from L to R)
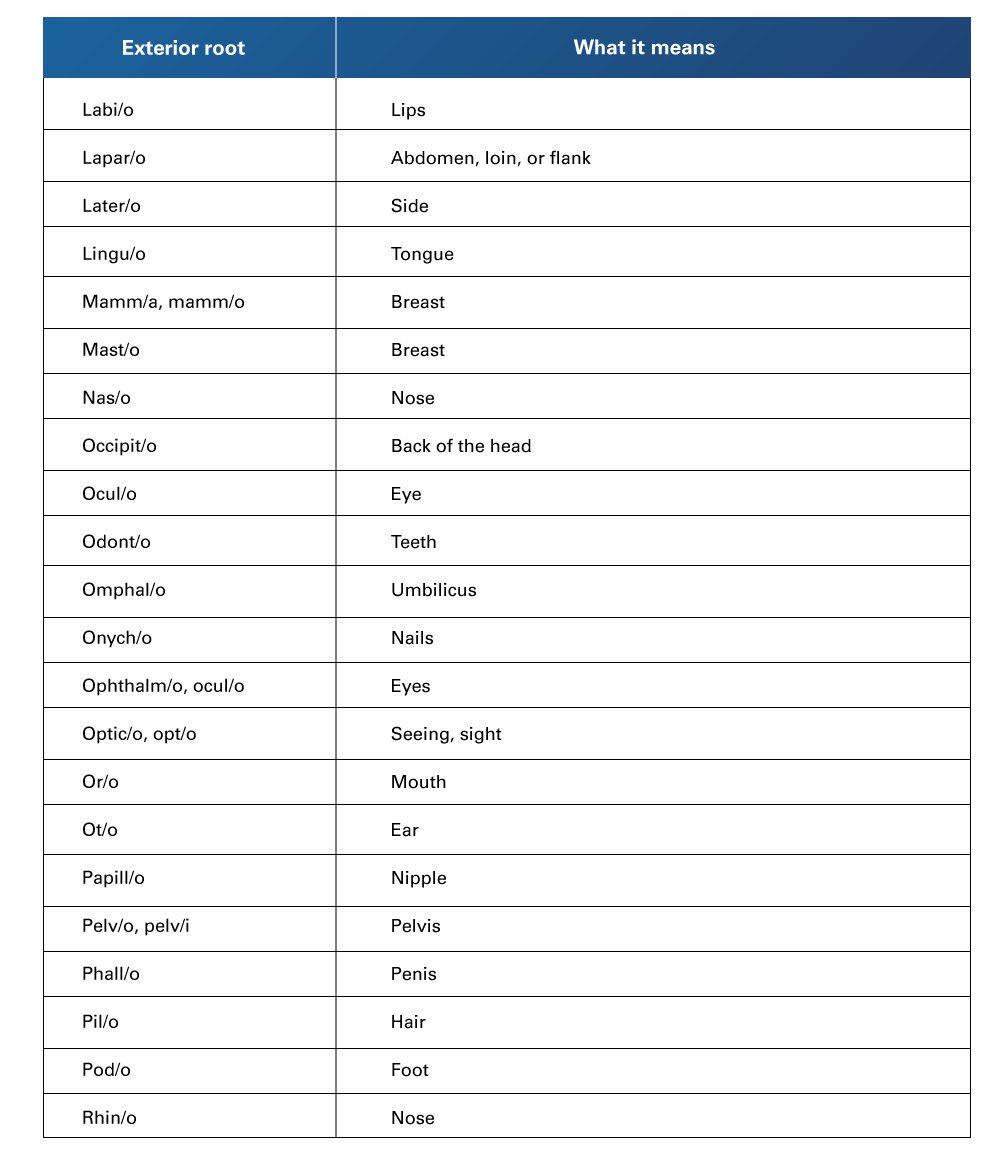 Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Table 3
Exterior Root Words and their Meaning (from S to V)
 Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Table 4
Interior Root Words and their Meaning (from A to M)
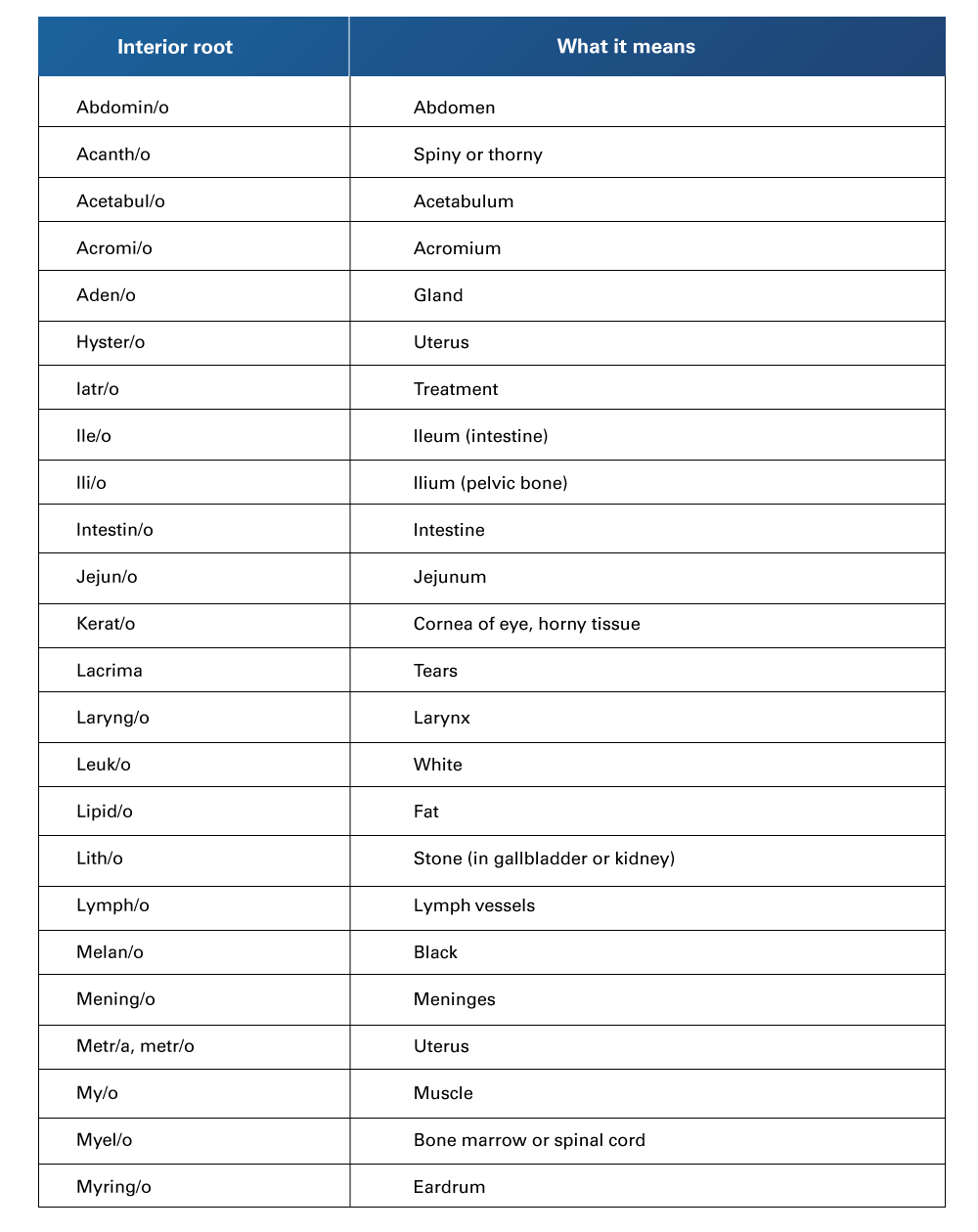 Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Table 5
Interior Root Words and their Meaning (from N to S)
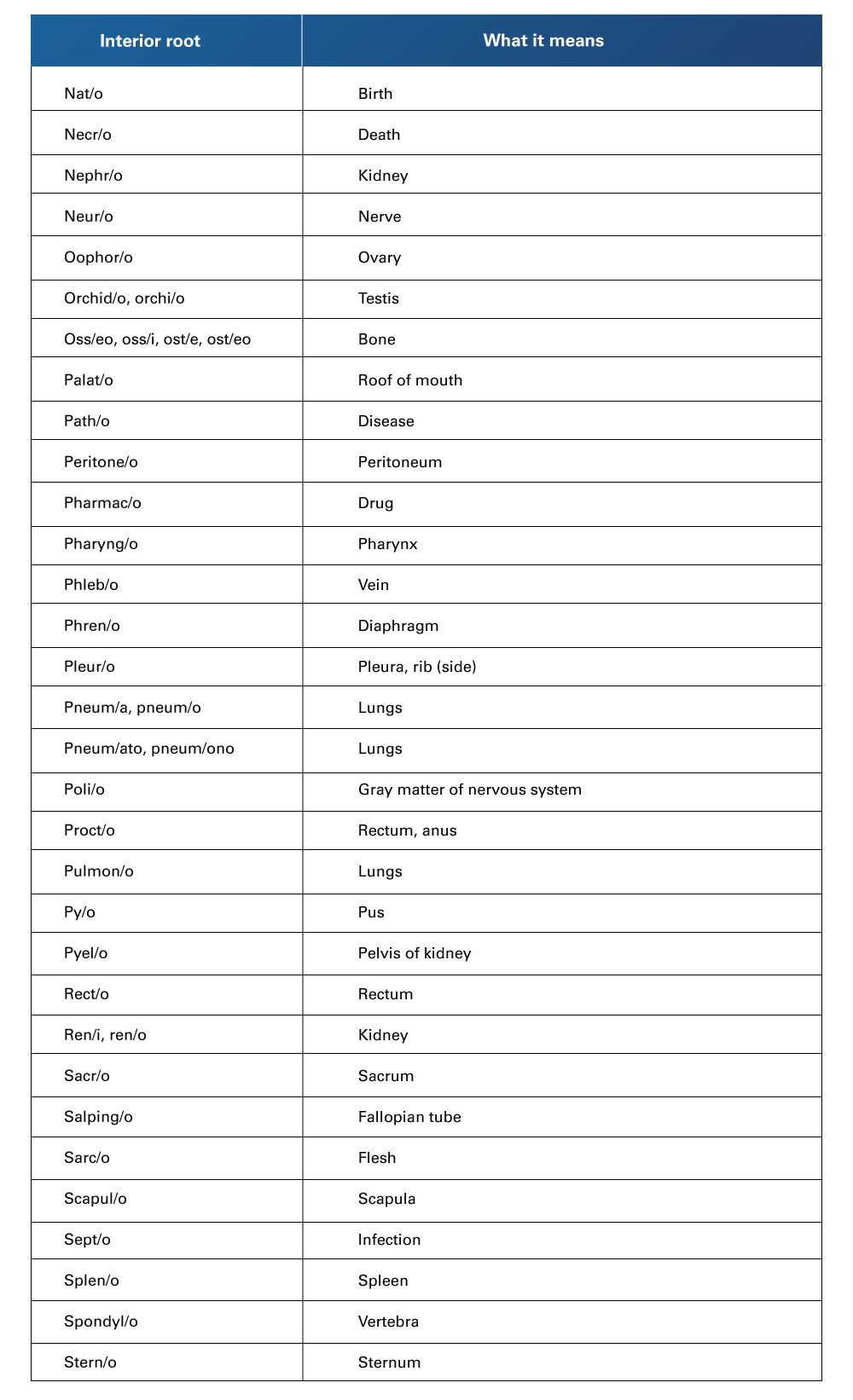 Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Table 6
Interior Root Words and their Meaning (from T to X)
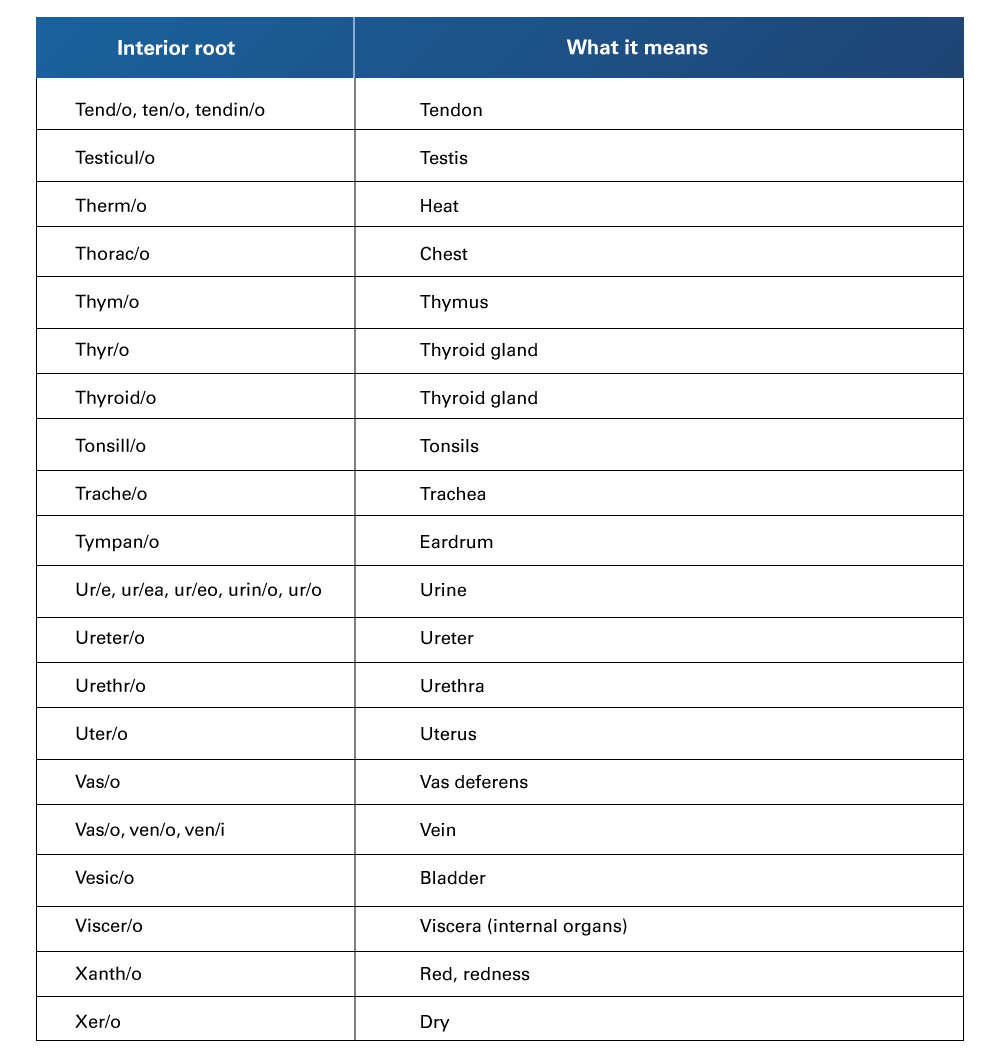 Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Retrieved from Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Table 7
Word origins
 Retrieved from Singh, N. (2016). Nursing: The Ultimate Study Guide (2nd ed.). Springer Publishing Company.
Retrieved from Singh, N. (2016). Nursing: The Ultimate Study Guide (2nd ed.). Springer Publishing Company.
Table 8
Word Root and Combining Vowels (a, e, i, o, u)
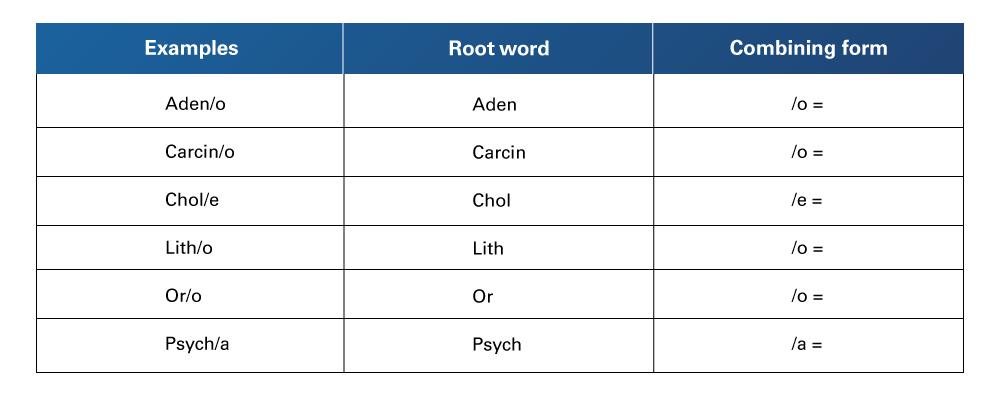 Retrieved from Singh, N. (2016). Nursing: The Ultimate Study Guide (2nd ed.). Springer Publishing Company.
Retrieved from Singh, N. (2016). Nursing: The Ultimate Study Guide (2nd ed.). Springer Publishing Company.
Table 9
Combining Form Vowels added to Word Roots when Attaching a Suffix that Begins with a Consonant or Another Word Root
 Retrieved from Crezee, I. (2013). Introduction to Healthcare for Interpreters and Translators. John Benjamins Publishing Company.
Retrieved from Crezee, I. (2013). Introduction to Healthcare for Interpreters and Translators. John Benjamins Publishing Company.
1.3 Clinical Terminology
In medicine, understanding medical terminology is crucial for effective communication and comprehension. Not grasping medical terms can be likened to being in a foreign country without the ability to communicate, evoking feelings of fear and hopelessness. The implications of misinterpreting clinical terminology can range from amusing mishaps, like a nurse donning a cervical collar instead of a lumbar brace, to severe consequences, such as administering the wrong medication to a patient with a history of anaphylactic shock.
Building a solid foundation of medical terms and learning how the medical language emerges enables effective communication in medicine.
Learning medical terms involves combining anatomical and physiological human body parts and creating new words that guide us to specific body regions and reveal important findings. Another approach to comprehend medical terminology is by identifying the healthcare professional responsible for treating the specific body part. Understanding medical terms helps in recognizing medical interventions and procedures, such as a cardiogram being a graphic recording of the heart.
Medical terminology is primarily based on Greek and Latin roots, prefixes, and suffixes, which guide the reader or listener to specific regions of the body or organs. As a clinician, mastering the basics of medical terminology is crucial for patient safety, as a small error in interpretation can have serious consequences.
As a clinician, you must ensure that you master the basics of medical terminology and understand that safety is essential.
The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHCO, n.d.) and NCSBN (2023) warn about easily mistaken words that increase the risk of injury. Memorizing the list in the resources section and using abbreviations cautiously is important for safe healthcare practice.
1.4 Common Healthcare Terms
Medical terminology is vast and complex; nevertheless, it is essential to get familiar with medicine and healthcare, including the written form used by the NCLEX. You will benefit from using the list of resources, but it is not exhaustive nor comprehensive in its entirety. The resources in the public domain, the world wide web, and personal textbooks are beneficial to successfully pass the NCLEX.
The following is a series of tables about medical terminology adapted from Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions (Nelson and Greene, 2021). We encourage you to review the complete book from Nelson and Greene, which is included in the bibliography section.
Table 10
Compilation of more Medical Terminology, from A to G
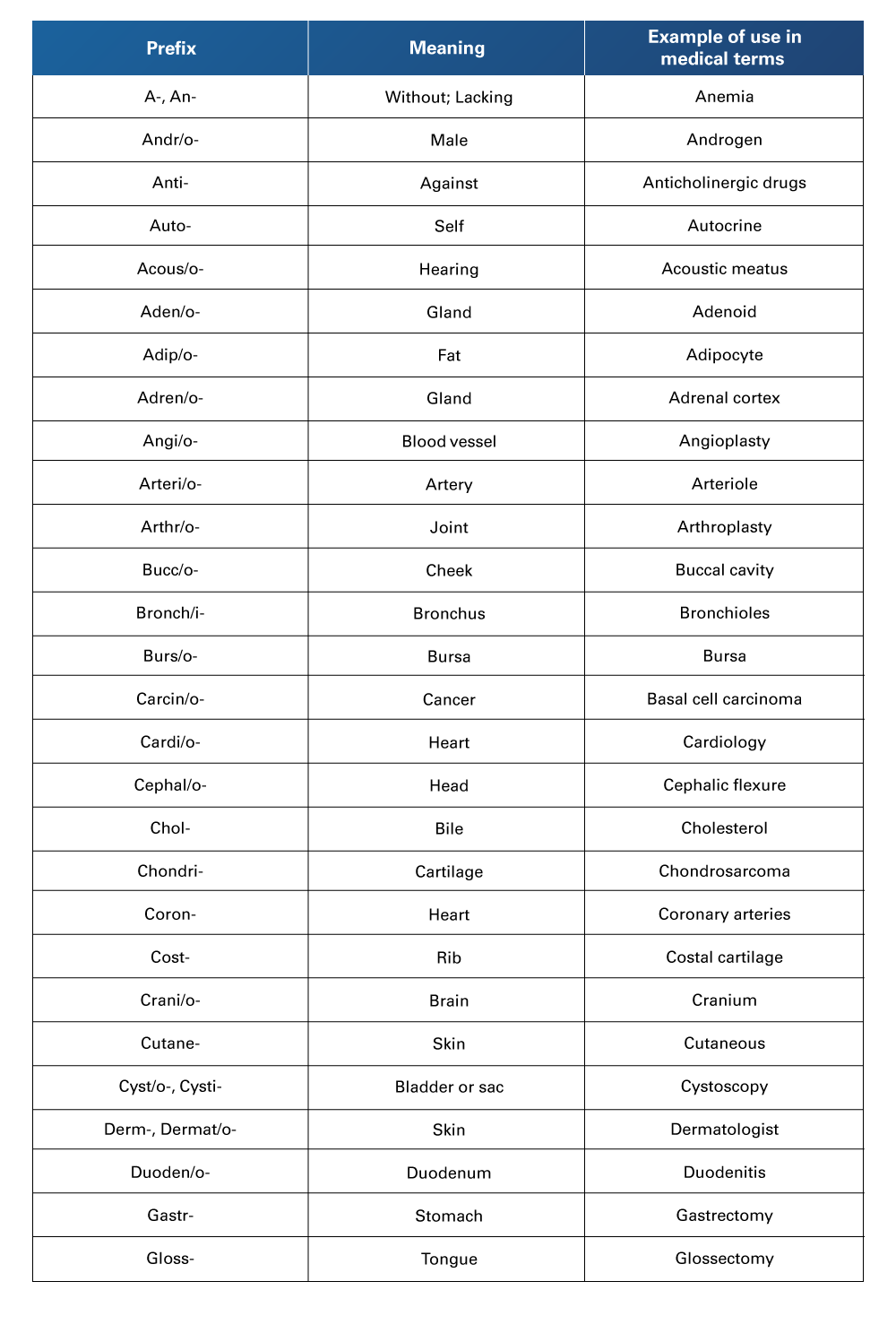 Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Table 11
Compilation of more Medical Terminology, from L to P
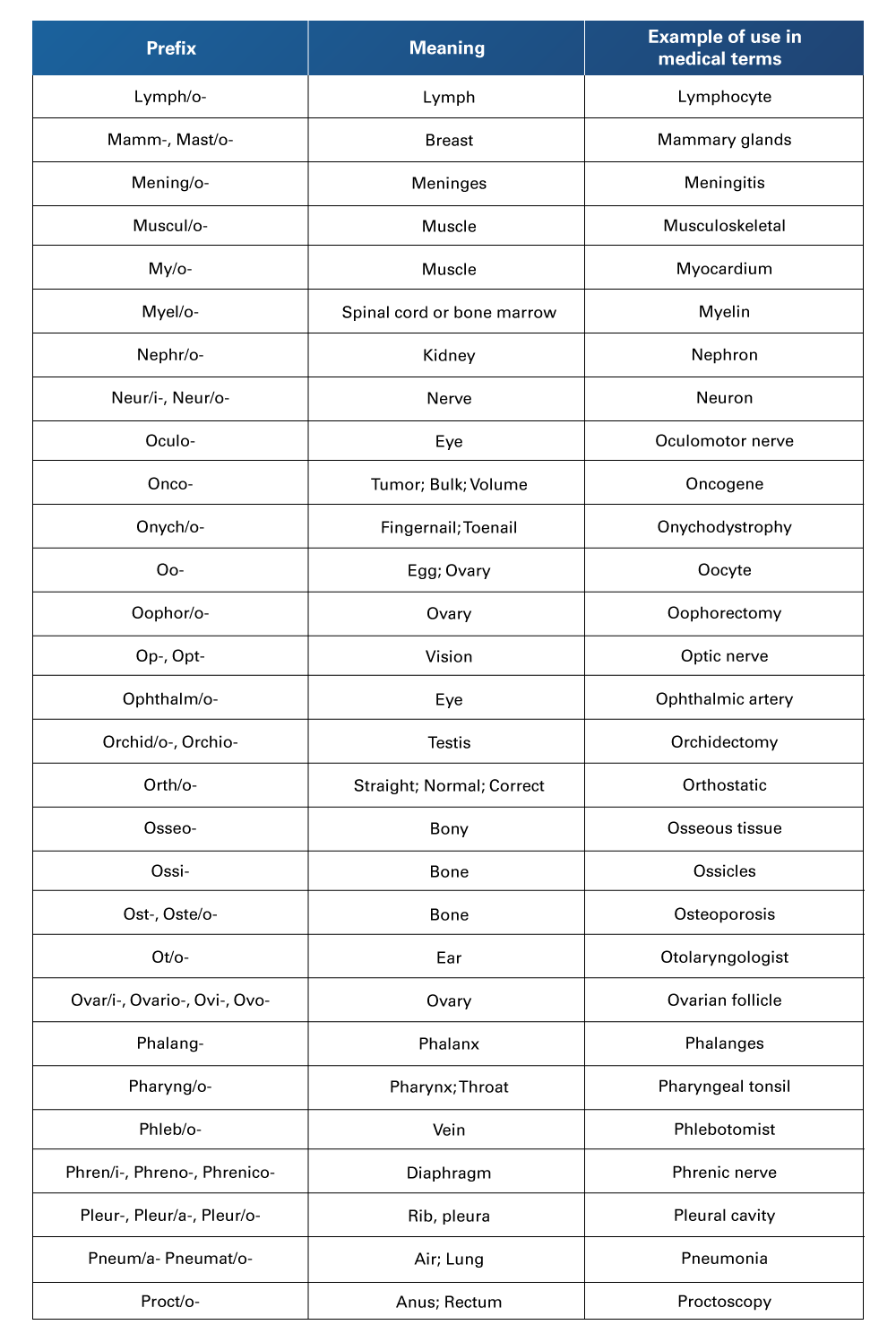 Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Table 12
Color Prefixes Used in Medical Terminology
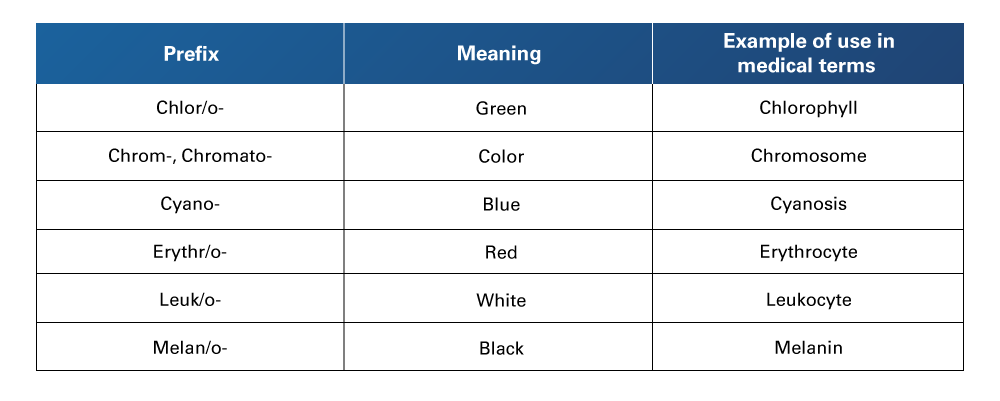 Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
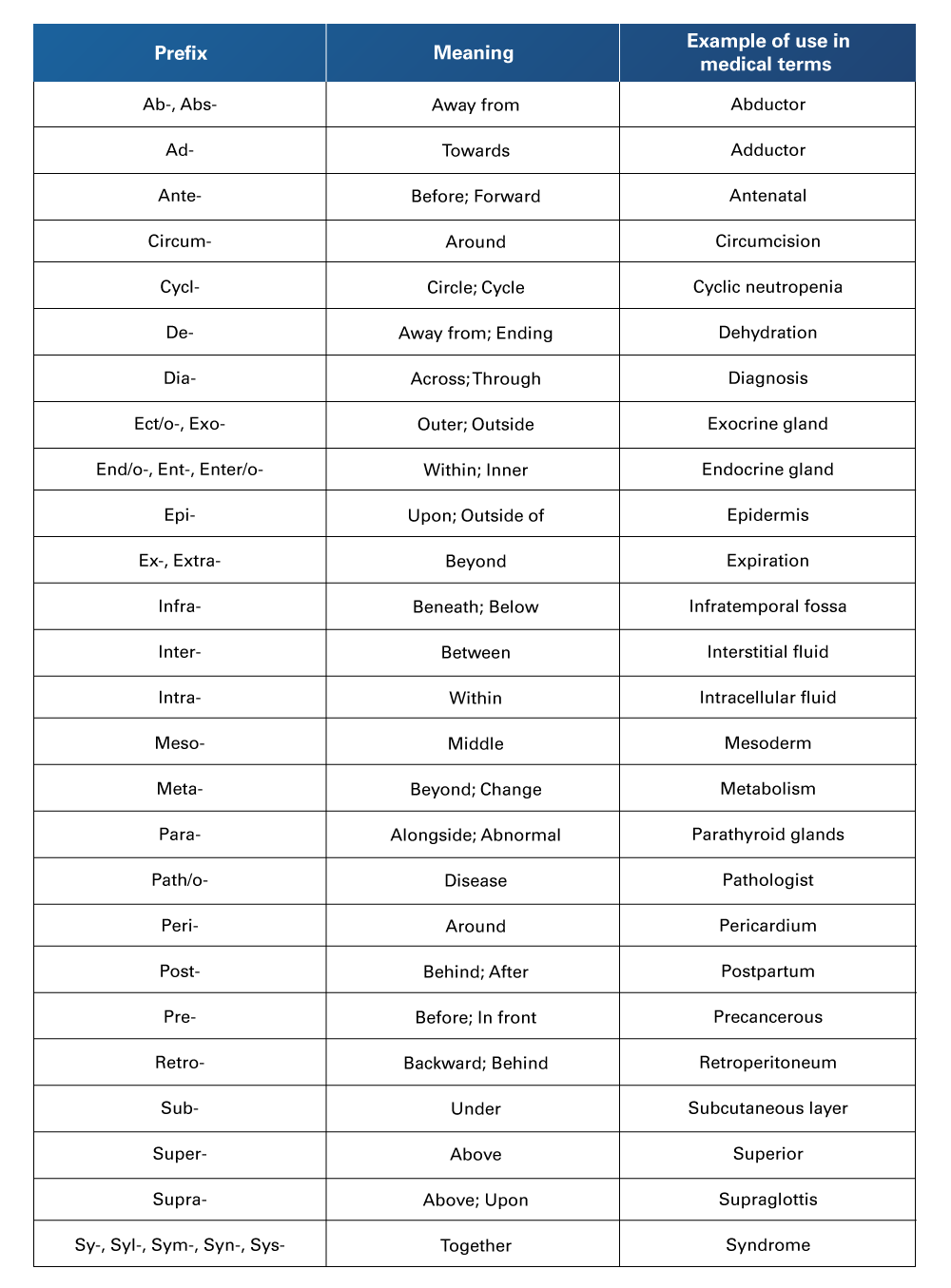
Table 13
State of Being Prefixes Used in Medical Terminology
 Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
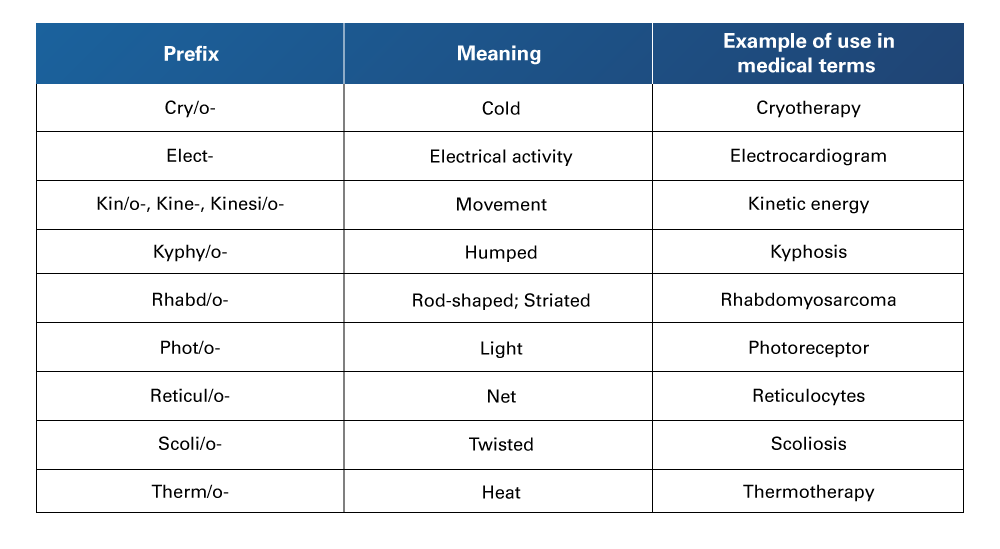
Table 14
Physical Property and Shape Prefixes Used in Medical Terminology
 Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Table 15
Quantities Prefixes Used in Medical Terminology
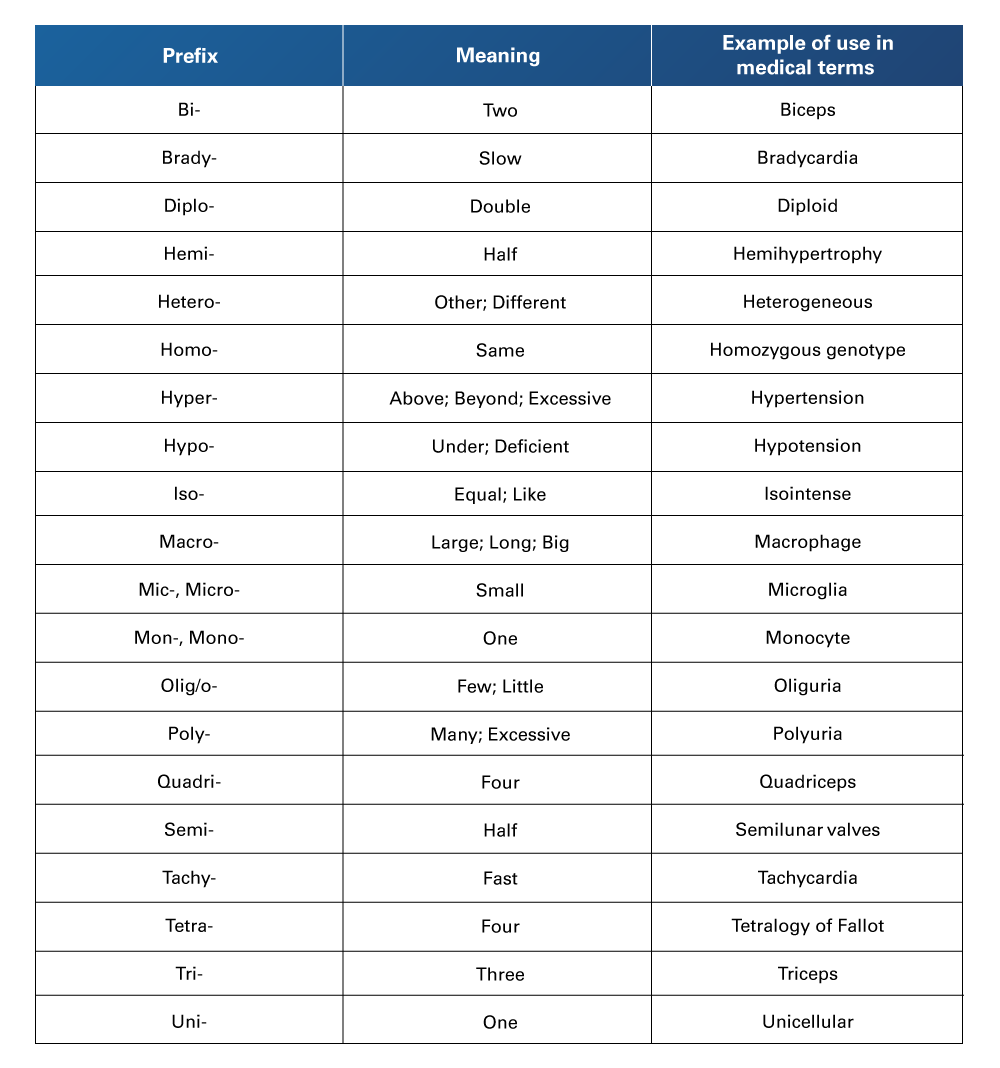 Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Table 16
Suffixes Used in Medical Terminology
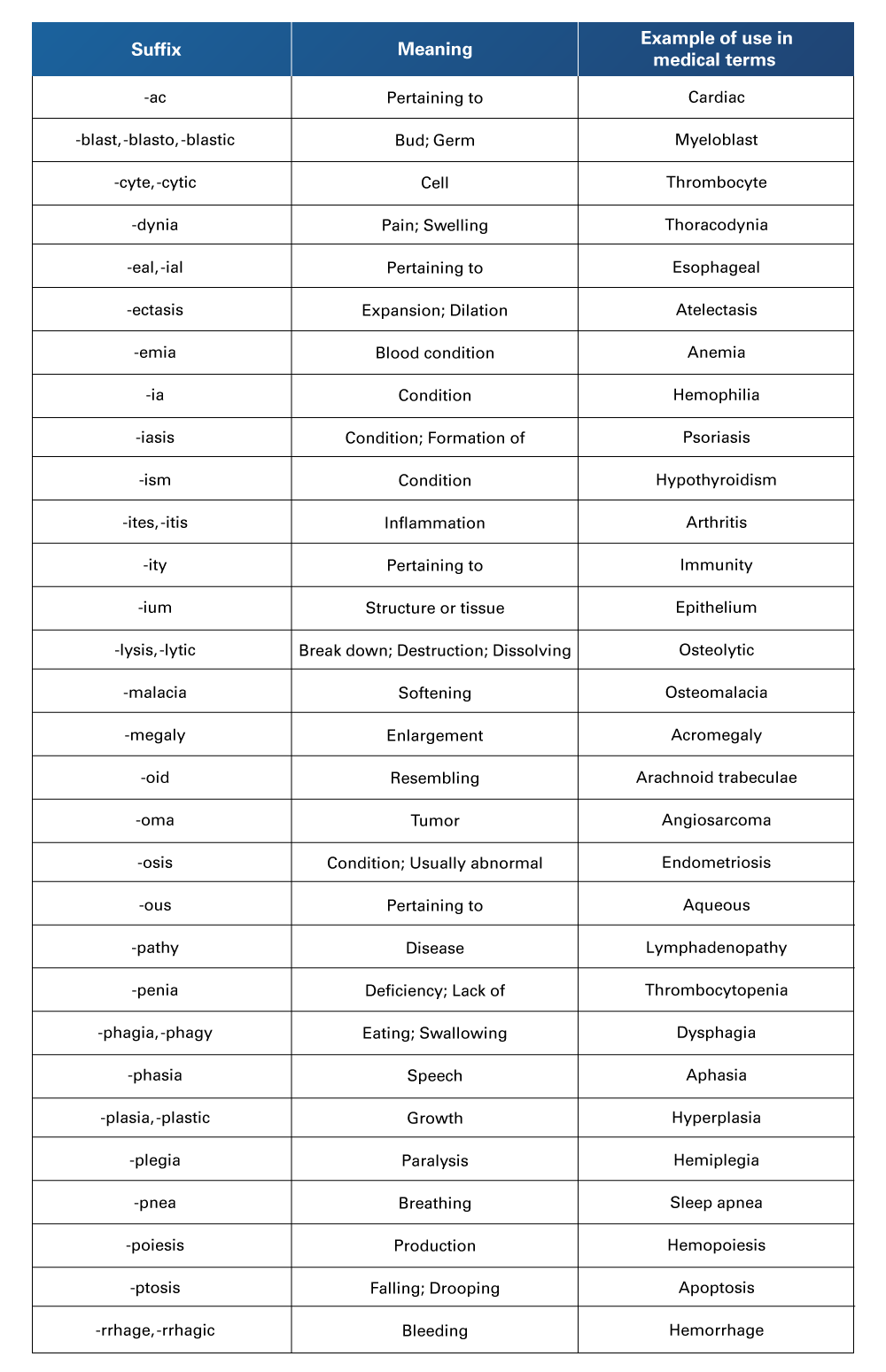 Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology
Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology
Table 17
Procedure Suffixes Used in Medical Terminology
 Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Retrieved from Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Medical Terms and NCLEX
In the NCLEX, expect questions testing your understanding of medical terms across various clinical areas. You must communicate, write, and comprehend in the language, medical terminology concerning anatomy, physiology, diseases, diagnostics, medications, and other healthcare concepts.
The National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX) incorporates questions that might be considered as “medical terminology,” seamlessly blending them into the exam. A prevailing theme throughout the NCLEX assessment is the essentiality of learners' or candidates' grasp of medical terms to logically infer and navigate the integrated processes fundamental to nursing. Effective communication and documentation are fundamental aspects of nursing care, encompassing oral, written, and linguistic language. Proficiency in medical terminology serves as a sturdy pillar supporting the nurse's clinical judgment, enabling them to adeptly recognize and interpret pertinent information, be it in real-life clinical scenarios or within the context of the NCLEX exam (NCSBN, 2023).
The NCLEX-style test question might look something like this:

In the NCLEX exam, multiple-choice questions may not explicitly indicate themselves as medical terminology questions. However, a profound understanding of medical words (sub+total; gastr+ectomy) within these questions becomes pivotal in deducing the correct answers, especially when equipped with knowledge of medical terminology.
The field of medical terminology is vast and continually evolving, encompassing an extensive lexicon that can pose challenges for aspiring healthcare professionals. To aid in this journey, we highly recommend exploring the invaluable work authored by Nelson and Greene, as referenced in the bibliography section. They have meticulously compiled a comprehensive downloadable book, serving as an Open Educational Resource which proves indispensable for any clinician seeking to master a Western English linguistic form of medical terminology. By delving into this resource, healthcare practitioners can enhance their proficiency in deciphering medical terms, thus bolstering their capabilities to successfully pass the rigorous NCLEX exam.
By the conclusion of this topic, you have solidified your understanding of medical terminology, becoming proficient in the language of healthcare. This linguistic journey has opened door to the captivating realm of medical terminology, all within comfort and security of your own safe space and welcoming atmosphere.
Increasing your ability to communicate and interpret meanings of anatomy, physiology, diseases process, treatments, and procedures is vital to ensure accurate patient care. crucial to make sure you understand and treat the patient correctly. Through practical applications and examinations, you gain proficiency in deciphering medical terms. The provided resources will enable you to continue expanding your medical vocabulary and its application in the medical field, ultimately leading to success in passing the NCLEX exam.
Confidence in your knowledge of medical terminology is crucial. Each one Each individual is the best judge of what of their level of understanding and medical terminology is needed required to be a safe and effective medical clinician, successfully passing the NCLEX examination.
Learning new languages is an exciting adventure. Now, at the end of this journey in learning medical terminology, you have the skills to auscultate for distention related to gastroparesis in the abdominopelvic area.
With a strong grasp of medical terminology, you can navigate the human body and all its components like a native speaker. Utilize the Open Education Resources (OER) and additional tools to master medical terminology, ensuring succeed in passing the NCLEX exam.
- Crezee, I. (2013). Introduction to Healthcare for Interpreters and Translators. John Benjamins Publishing Company.
- Daly, J., Speedy, S., Jackson, D., Lambert, V., & Lambert, C. (Eds.). (2005). Professional Nursing: Concepts, Issues, and Challenges. Springer Publishing Company.
- Henderson, B., & Dorsey, J. L. (2019). Medical terminology for dummies. John Wiley & Sons. https://books.google.com.mx/books?hl=es&lr=&id=7Ky5DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA3&dq=medical+terminology+for+dummies&ots=Z8jc3yh5jt&sig=qo_eKkQVwC5x-vmgFLCL06heCTY&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=medical%20terminology%20for%20dummies&f=false
- Jóskowska, K., & Grabarczyk, Z. (2013). Greek and Latin in medical terminology. Medical Research Journal, 1(2), 41-52. https://journals.viamedica.pl/medical_research_journal/article/view/36871
- Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (2018). Lippincott visual nursing: A guide to clinical diseases, skills, and treatments (3rd ed.). Wolters Kluwer.
- Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
- Pepper, O. H. (n.d.). The History of Medical Terminology. Openmd.com. https://openmd.com/guide/history-of-medical-terminology
- Singh, N. (2016). Nursing: The Ultimate Study Guide (2nd ed.). Springer Publishing Company.
- UHEROVá, Z., & Horňáková, A. (2013). Medical terminology and its particularities. Jahr–European Journal of Bioethics, 4(1), 631-638.
The following links do not belong to Tecmilenio University, when accessing to them, you must accept their terms and conditions.
Videos
To view 75 question practice tests for the NCLEX exam, watch the following video:
- Boone Academy. (2022, March 28). NCLEX-RN Full Practice Test - 1 | 2023 | 75 Questions with Explained Answers and timer [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/370P2AnqysE
Readings
- McAllister, N., Tavener-Smith, T., & Williams, J. (2022). Roots, prefixes, and suffixes: decoding medical terminology using an online enquiry-based learning intervention for nursing associates. Teaching and Learning in Nursing, 17(3), 256-262.
- NCSBN. (2022). NCLEX Test Plan 2023.https://www.ncsbn.org/publications/2023-nclex-rn-test-plan
- Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/chapter/prefixes-and-suffixes/
- Schroeder, C, L., Ehrich, L., Schroeder, K., & Ehrich, A. (2022). Medical Terminology for Health Professions (9th ed.). Cengage.
La obra presentada es propiedad de ENSEÑANZA E INVESTIGACIÓN SUPERIOR A.C. (UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO), protegida por la Ley Federal de Derecho de Autor; la alteración o deformación de una obra, así como su reproducción, exhibición o ejecución pública sin el consentimiento de su autor y titular de los derechos correspondientes es constitutivo de un delito tipificado en la Ley Federal de Derechos de Autor, así como en las Leyes Internacionales de Derecho de Autor.
El uso de imágenes, fragmentos de videos, fragmentos de eventos culturales, programas y demás material que sea objeto de protección de los derechos de autor, es exclusivamente para fines educativos e informativos, y cualquier uso distinto como el lucro, reproducción, edición o modificación, será perseguido y sancionado por UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO.
Queda prohibido copiar, reproducir, distribuir, publicar, transmitir, difundir, o en cualquier modo explotar cualquier parte de esta obra sin la autorización previa por escrito de UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO. Sin embargo, usted podrá bajar material a su computadora personal para uso exclusivamente personal o educacional y no comercial limitado a una copia por página. No se podrá remover o alterar de la copia ninguna leyenda de Derechos de Autor o la que manifieste la autoría del material.