Medical Terminology / 02
Make sure to:
- Recognize and essential manage the concepts and language specific to the ability to integrate the medical terminology knowledge relating to the Nursing Process.
- Achieve proficiency in the nursing context, concepts, and language to effectively explain and communicate, linking previously learned frameworks to successfully pass the NCLEX exam.
- Retrieve and apply knowledge in a practical situation to solve a challenge or project faced under a specific healthcare management.
Nursing terminology, concerning medical terminology and the impact or implication of successfully passing the NCLEX in the United States, has much to do with mastering the universal language of medicine and the human physiological and anatomical lingo healthcare practitioners use to communicate safely and effectively in the health field. When healthcare professionals can communicate clearly and precisely with one another, it improves patient care and advances the healthcare system as a whole.
 Moreover, the primary mission of the Board of Nursing (BON) is to safeguard the public health (NCSBN, n.d.). As such, the implication of obtaining a nursing licensure credential is to ensure that a nurse possesses the minimum intellectual capacity required to practice safely. Additionally, the ability to apply the foundational principles of the nursing process, assimilating in the nursing context using healthcare management terminology and theories, is crucial for delivering effective and efficient patient care. Now, the question arises: Are you ready to pass your NCLEX? In addition to demonstrating your knowledge and comprehension of nursing topics, passing the NCLEX exam is a sign of your dedication to giving your patients safe, competent care. If you actively prepare yourself, you will set the route for a rewarding and successful nursing profession.
Moreover, the primary mission of the Board of Nursing (BON) is to safeguard the public health (NCSBN, n.d.). As such, the implication of obtaining a nursing licensure credential is to ensure that a nurse possesses the minimum intellectual capacity required to practice safely. Additionally, the ability to apply the foundational principles of the nursing process, assimilating in the nursing context using healthcare management terminology and theories, is crucial for delivering effective and efficient patient care. Now, the question arises: Are you ready to pass your NCLEX? In addition to demonstrating your knowledge and comprehension of nursing topics, passing the NCLEX exam is a sign of your dedication to giving your patients safe, competent care. If you actively prepare yourself, you will set the route for a rewarding and successful nursing profession.
 At the end of this comprehensive learning experience, you will not only demonstrate a profound and thorough understanding of the specific terminology, fundamental concepts, and specialized language used in the context of health sciences applied to nursing but also gain the necessary skills and confidence to excel in the NCLEX certification exam.
At the end of this comprehensive learning experience, you will not only demonstrate a profound and thorough understanding of the specific terminology, fundamental concepts, and specialized language used in the context of health sciences applied to nursing but also gain the necessary skills and confidence to excel in the NCLEX certification exam.
To prepare yourself for the NCLEX exam, you will have to study a range of crucial nursing topics, such as anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and patient care methods. A robust foundation of knowledge that goes beyond simple memorization will be provided by the curriculum, enabling you to evaluate difficult situations critically and draw well-informed clinical findings.
Remember, your path to nursing excellence begins here. Are you prepared to take it on totally and seize the myriad chances that lie ahead for you in the healthcare industry?
In this topic, you will explore the crucial link between medical terminology and nursing, examining how it seamlessly integrates into various aspects of the nursing profession. By immersing yourself in the nursing process and understanding its application in different healthcare contexts, you will develop a profound appreciation for the significance of medical terminology in delivering optimal patient care.
Notably, Florence Nightingale—known as the "mother of nursing"—started modern nursing as we know it in the middle of the 1800s (Daly et al., 2005). Nursing techniques used today have their roots in Nightingale's innovative work in healthcare. She had a strong tendency to maintain thorough records, record nursing interventions, and assess nurses' performance. Nightingale's dedication to evidence-based practice was shown by her constant inquiry of “Did it work or not?”. This emphasis on record-keeping and documentation of daily activities gave rise to what we now know as the nursing process. Scholars Daly et al. (2005) describe the nursing process as a conceptualized and organized tool for clinical decision-making, fostering critical thinking among nurses.
Florence Nightingale continues to have an impact on modern nursing, emphasizing the value of data-driven decision-making and the constant pursuit of patient care high standards. The nursing quality foundations and patient safety remain Nightingale's scrupulous recordkeeping and ideals of evidence-based practice.
Recognizing the critical importance of safe and effective patient care, the Board of Nursing (BON) confirms that the nursing process stands as an indispensable cognitive skill (NCSBN, n.d.).
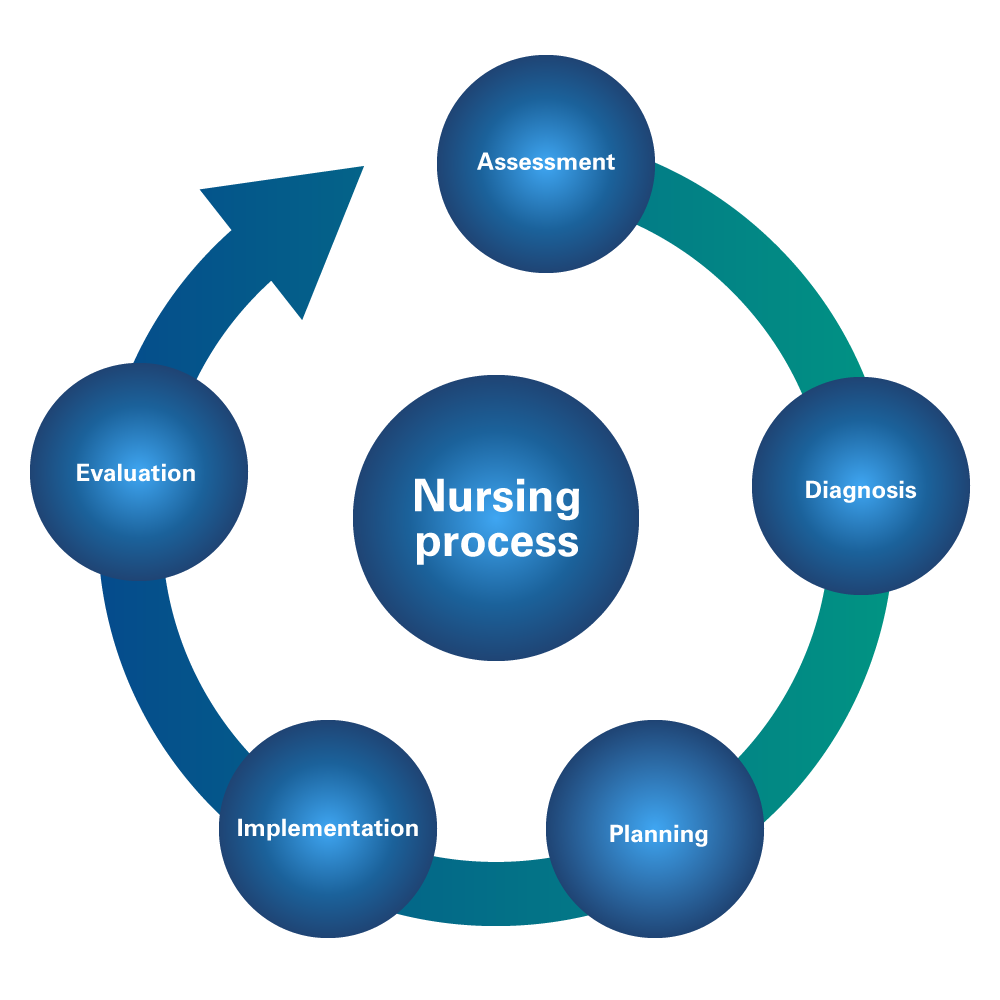
The nursing process, which is grounded on evidence-based practice, acts as a systematic approach that directs nurses in providing thorough and patient-centered care. It includes assessment, diagnosis, planning, execution, and evaluation, ensuring a systematic approach to the healthcare delivery.
The BON has established that NCLEX item questions align with the mission of safeguarding the public welfare. Therefore, by specifying the standards beforehand and determining whether licensing applicants meet them, the licensure procedures are created to assure the safety and effectiveness of candidates.
The following case scenario highlights the critical role of medical terminology in nursing practice. It also emphasizes the context in which this scenario unfolds and, ultimately, the significance of medical terminology as the language of communication navigation, and healthcare management.
In this case, using appropriate medical terminology is crucial for communicating correct information about a patient's health, symptoms, and course of treatment. Nurses who are fluent in medical terminology are better able to collaborate with other medical specialists and provide seamless patient care.
Figure 1
Case Scenario 1: Cardiovascular Accident (CVA)
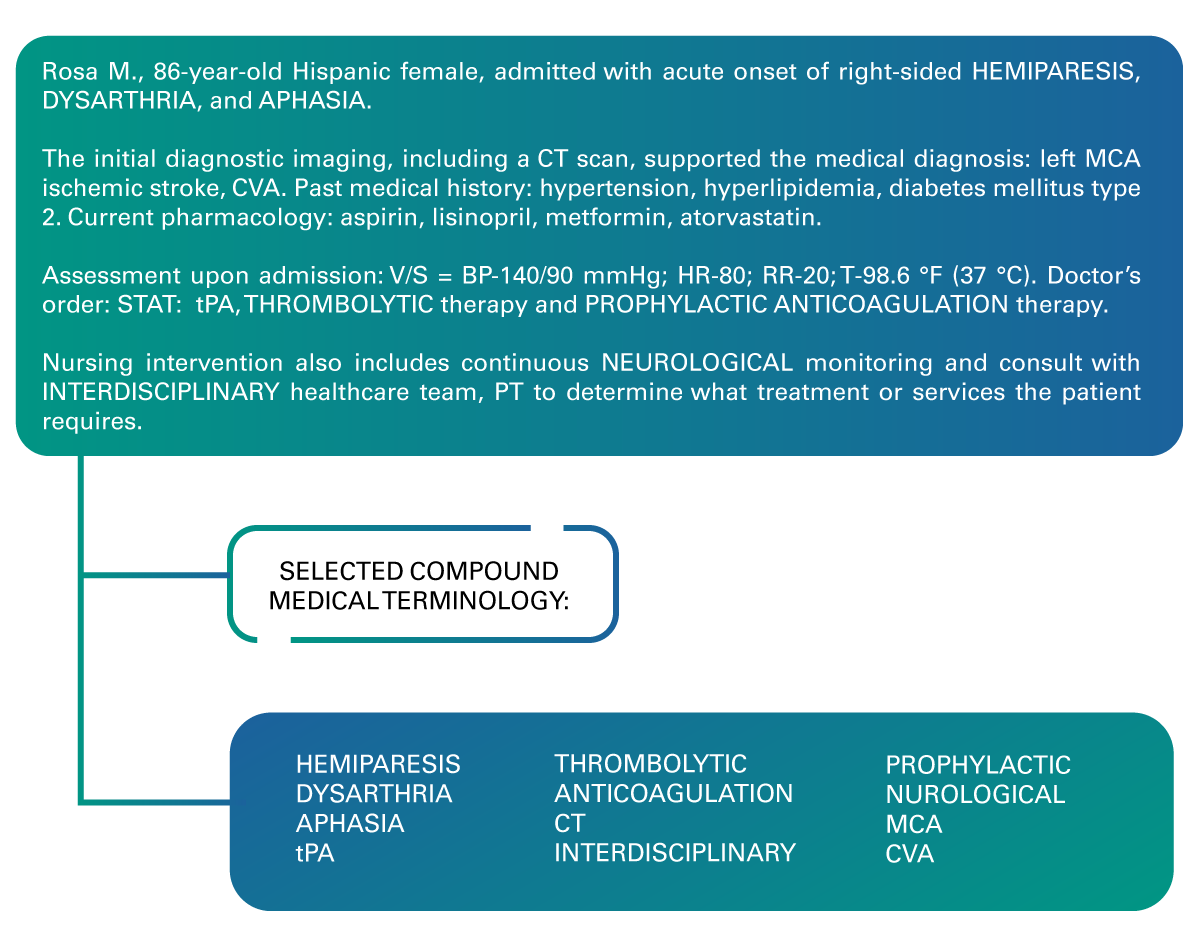
2.1 Nursing Process
Influenced by medical and scientific terminology and methods, the nursing process and medical terminologies are interconnected. Both of these elements play crucial roles in healthcare management. For instance, when our 86-year-old-female patient is discharged from the acute setting or hospital, she encounters significant number of diverse healthcare team members. Additionally, upon discharge, these team members continue to deliver healthcare in alternative settings (such as clinics and rehabilitation centers), thereby altering the contextual environment. Nonetheless, they ensure that communication remains open and accurate.
Medical terminology offers nursing a substantial advantage through the inclusion of descriptive verbs that elucidate nurses' actions within healthcare management. The following figure illustrates the five primary actions that predominantly underpin the nursing process and its interconnections.
Figure 2
Nursing Process: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation and Evaluation
To better illustrate each step of the nursing process, check the following example that describes a tangible scenario:
As you arrive at your workstation, you begin by:
- Assess: Which tasks require immediate attention and remain pending?
- Diagnose: the requirement for supplementary resources. Are there alternative avenues worth exploring? Outsourcing emerges as a promising option.
- Plan: Delegating specific tasks to an external service provider appears as the optimal course of action.
- Moving forward, embark on orchestrating the essential arrangements to enlist the external service (Implement).
- Finally, Evaluate the outcome: Did the outcome align with expectations? Certainly, the tasks were not only efficiently accomplished but also facilitated a smoother workflow.
This illustration effectively highlights the intricate interrelation between routine decision-making and the meticulous nursing process, encompassing a refined professional tone while accentuating the pivotal stages that constitute it.
Moreover, the acronym ADPIE (Ackley & Ladwig, 2010) which compresses the fundamental tenets of the nursing process, serves as a compass guiding nurses in comprehending the multifaceted needs of their patients and in formulating the most suitable course of action for their care. In a similar way the daily challenges that nurses encounter, where they consistently strive to make judicious decisions to ensure the utmost safety and comprehensive well-being of their patients (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2018; Singh, 2016).
Table 1
ADPIE: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Implantation, Evaluation
 Retrieved from Ackley, B. J., & Ladwig, G. B. (2010). Nursing diagnosis handbook: An evidence-based guide to planning care. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Retrieved from Ackley, B. J., & Ladwig, G. B. (2010). Nursing diagnosis handbook: An evidence-based guide to planning care. Elsevier Health Sciences.
As a nurse assigned to Rosa, what takes priority? What will be your initial course of action? Are you able to interpret pertinent data, such as vital signs? Numerous NCLEX-style questions assess a nurse's critical thinking concerning prompt responses. By utilizing the terminology of the nursing profession, you can communicate with the healthcare management team in the patient care setting both securely and proficiently.
2.2 Nursing context
A more in-depth analysis of the context of the case scenario which unfolds solely within an acute care setting or hospital, offers a single exemplar of a milieu. However, to comprehensively enrich your clinical practice, it's imperative to delve into further research and assimilate relevant subjects’ (e.g., clinic, nursing, etc.) daily. Context refers to the background against which the nurse/patient relationship evolves, and it is significance lies in effective communication, precise documentation, and the delivery of high-quality care (Daly et al., 2005; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2018; Singh, 2016).
Let's go through the Case Scenario 1 again for additional analysis and synthesis:
Rosa M., 86-year-old Hispanic female, admitted with acute onset of right-sided HEMIPARESIS, DYSARTHRIA, and APHASIA. The initial diagnostic imaging, including a CT scan, supported the medical diagnosis: left MCA ischemic stroke, CVA. Past medical history: hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus type 2. Current pharmacology: aspirin, lisinopril, metformin, atorvastatin. Assessment upon admission: V/S = BP-140/90 mmHg; HR-80; RR-20; T-98.6 °F (37 °C). Doctor’s order: STAT: tPA, THROMBOLYTIC therapy and PROPHYLACTIC ANTICOAGULATION therapy. Nursing intervention also includes continuous NEUROLOGICAL monitoring and consult with INTERDISCIPLINARY healthcare team, PT to determine what treatment or services the patient requires.
Subsequently, analyze each nursing context in relation to communication, patient-centered care, interdisciplinary healthcare team, patient education, and patient-centered goals. Examine how these aspects intertwine with medical terminology within the broader concept of context.
Figure 3
Nursing Process: Communication, Patient-centered Care, Interdisciplinary Healthcare Team, Patient Education, and Patient-centered Goals
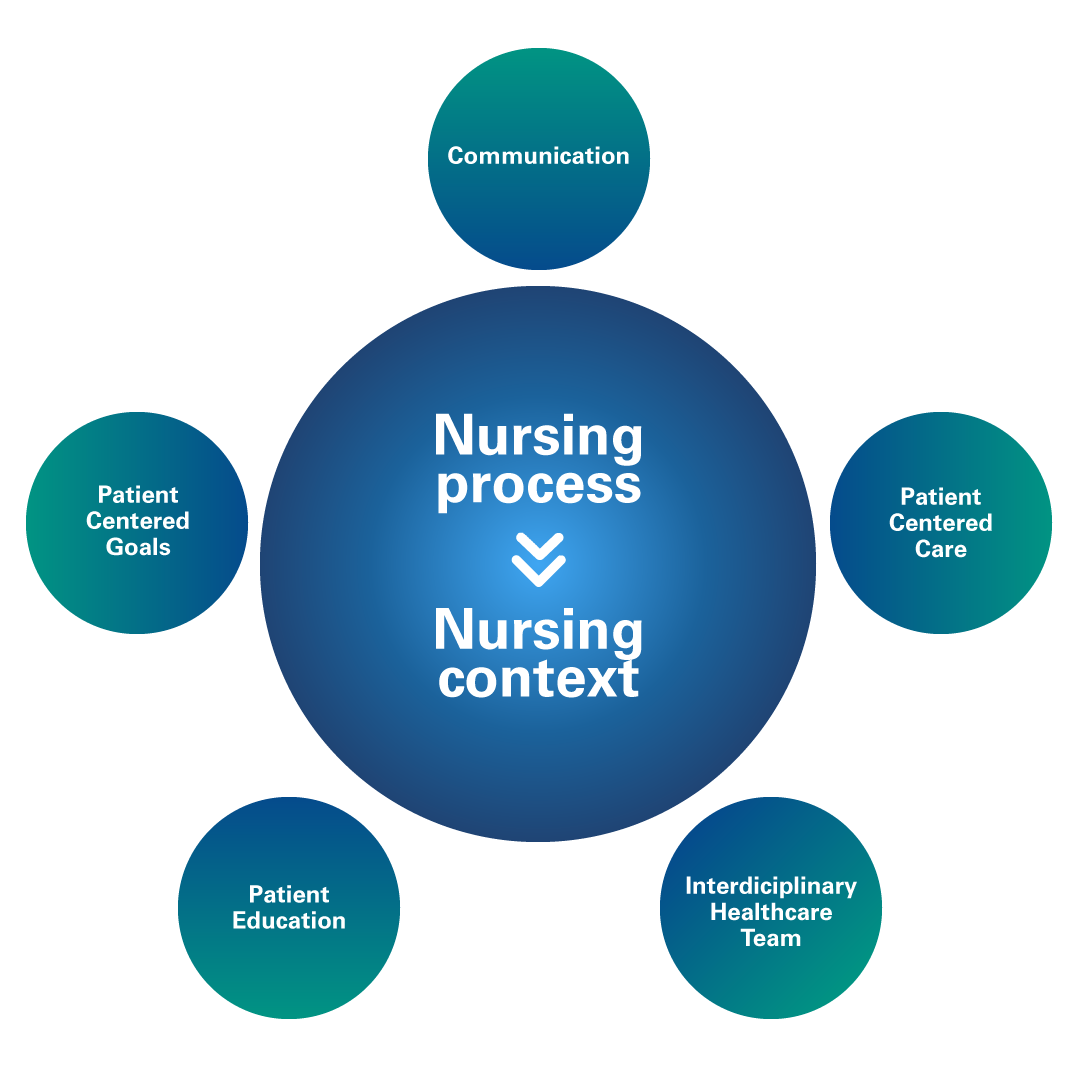
Communication:
Nurses employ medical terminology for effective communication among healthcare professionals through written and verbal means. In the case given scenario 1, when the doctor prescribes a CT scan, it is crucial for the nurse to understand that a CT scan stands for Computer Tomography (Singh, 2016).
Patient-centered care:
This context is centered on the patient, emphasizing the assistance required for the patient to achieve optimal functionality. In this scenario, medical terminology highlights the abbreviation PT, denoting Physical Therapy (Singh, 2016).
Interdisciplinary healthcare team:
Within the nursing context, collaboration with diverse healthcare professionals is frequent. Nurses can effectively establish communication channels with physicians, therapists, social workers, and various other members of the healthcare team members by having a solid understanding of medical terminology. This proficiency fosters a multidisciplinary approach to patient-centered care, enabling all stakeholders to exchange cohesively and interpret it uniformly. This collective effort significantly contributes to the patient's optimal outcome (Daly et al., 2005; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2018; Singh, 2016).
Patient education:
Nurses play a crucial role educating patients and their families about their health conditions, treatments, and self-care practices. Medical terminology equips nurses to elucidate medical concepts, procedures, and medication instructions in a manner that patients can comprehend. By employing familiar medical terms, nurses empower patients to actively engage in their care journey and make well-informed decisions.
Patient-centered goals:
Patient and their caregivers must establish a foundation of trust with the nurse while collectively defining achievable goals tailored to the patient´s capabilities. It is the nurse's duty to vigilantly monitor the patient's progress and response. Additionally, they should factor in the patient's age, demographics, and educational background while crafting patient-centered care plan objectives, ensuring a therapeutic rapport and effective communication. However, nurses need to comprehend medical terminology and adeptly rephrase it for patient comprehension. For instance, does the patient comprehend the term “thrombolytic”? How will the nurse proficiently deconstruct it into its root word, prefix, and suffix delivering a concise and clear explanation? Proficiency in medical terminology enables the alignment of patient-centered goals (Daly et al., 2005; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2018; Singh, 2016), fostering a more effective therapeutic alliance.
2.3 Healthcare Management Terminology
Figure 4
Healthcare Management Terminology
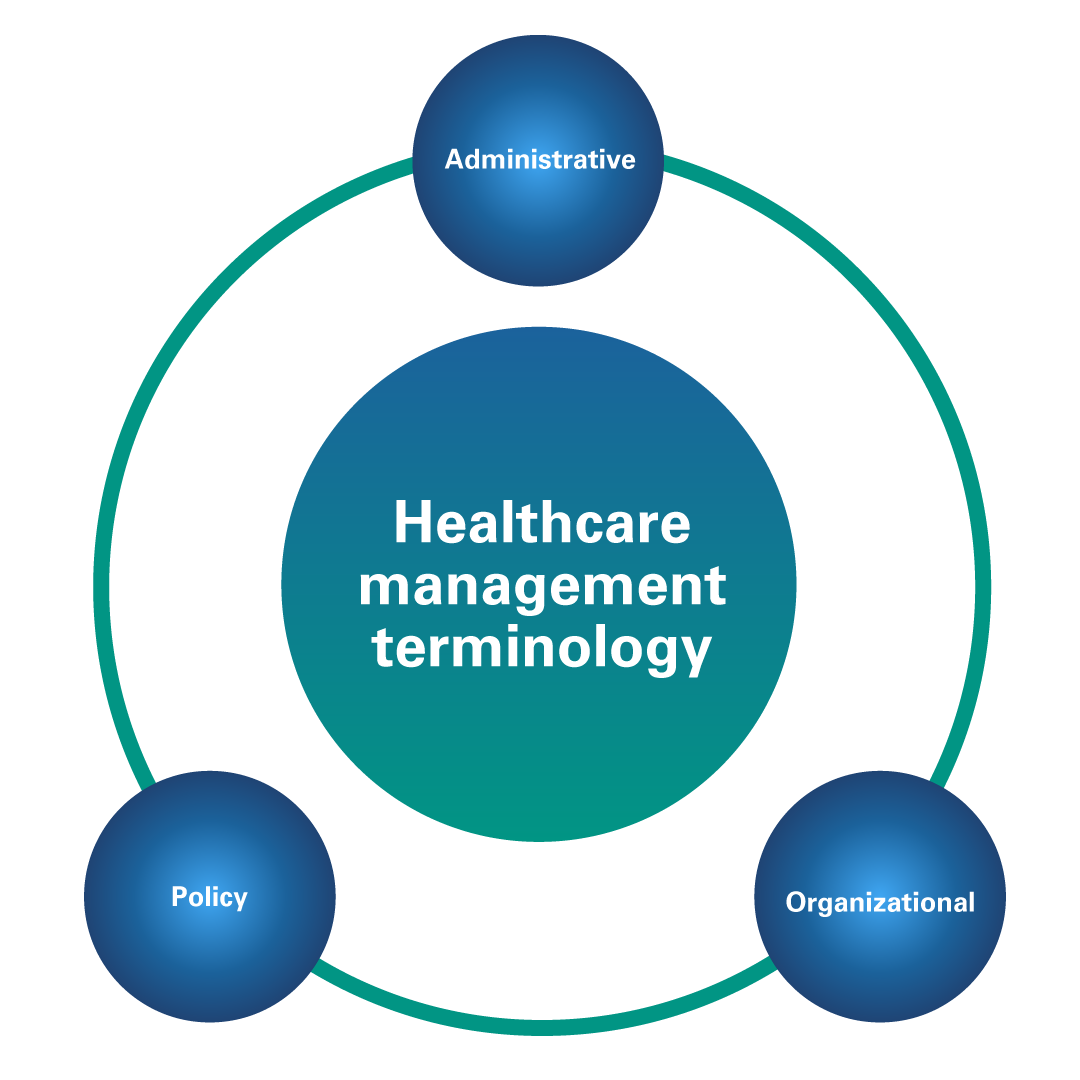
Healthcare management terminology refers to the specific vocabulary and terminology employed within the medical field. This encompasses concepts, principles, administrative procedures, organizational structures, and policy-related terminology. The field of healthcare management is extensive, housing numerous additional specialized terms and concepts. The examples provided here serve as an example of healthcare management terminology.
Administrative: Administrative responsibilities within healthcare involve nurses overseeing and managing and overseeing the operations of healthcare entities, such as hospitals, clinics, or healthcare systems. For instance, serve as professionals in charge of operational aspects, financial management, and human resources. In the context of managing the healthcare manager needs of an 86-year-old Hispanic female, nurses hold the responsibility of determining whether the patient requires Medicaid, Medicare, or insurance coverage. They also assess if the patient is underinsured or facing resource limitations. If the patient is underinsured or if the patient falls indigent of resources. These scenarios introduce new terms into the nurse's vocabulary, aligning with the evolving language of medical terminology (Daly et al., 2005; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2018; Singh, 2016). As front-line healthcare providers, nurses play a key role in navigating complex administrative complexities to ensure comprehensive patient care.
Organizational: Organizational context refers to a collective or entity that offers healthcare services, encompassing hospitals, medical practices, nursing homes, or health systems. When formulating NCLEX test questions, precision and clarity concerning the item's context are paramount. The analysis of the context plays a vital role in clinical decision-making. For instance, as Rosa is discharged from the hospital, she could transition to a rehabilitation center, where her health progress becomes the primary goal rather than the acute exacerbation monitoring. The shift in focus highlights the importance of recognizing the evolving healthcare setting and aligning care goals accordingly.
Policy: frequently involves the collaboration of nurses and various healthcare team members. It involves the creation of rules, regulations, and guidelines established by government bodies, healthcare organizations, or professional associations. These policies serve as guiding principles for healthcare delivery, reimbursement processes, and decision-making within the healthcare field (Daly et al., 2005; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2018; Singh, 2016).
Healthcare management terminology provides the framework for communication, guiding the process of directing and connecting Rosa, our 86-year-old Hispanic female, within the extensive network of organizations integral to the healthcare system. Rosa will uphold a regimen of follow-up appointments and rehabilitation, adhering to established policies. This could encompass visits to specialized clinics like cardiologists, sessions for vascular disease management and physical therapy, as well as home health nursing services, among others. This comprehensive approach ensures Rosa's ongoing care aligns seamlessly with the broader healthcare environment.
To assist in navigating this language, below you will be able to find a series of concise tables, each highlighting key medical terms and their meanings. These tables cover a range of essential concepts, from nursing specialties and diagnostic procedures to medical abbreviations and equipment.
Table 2
General Nursing Terms
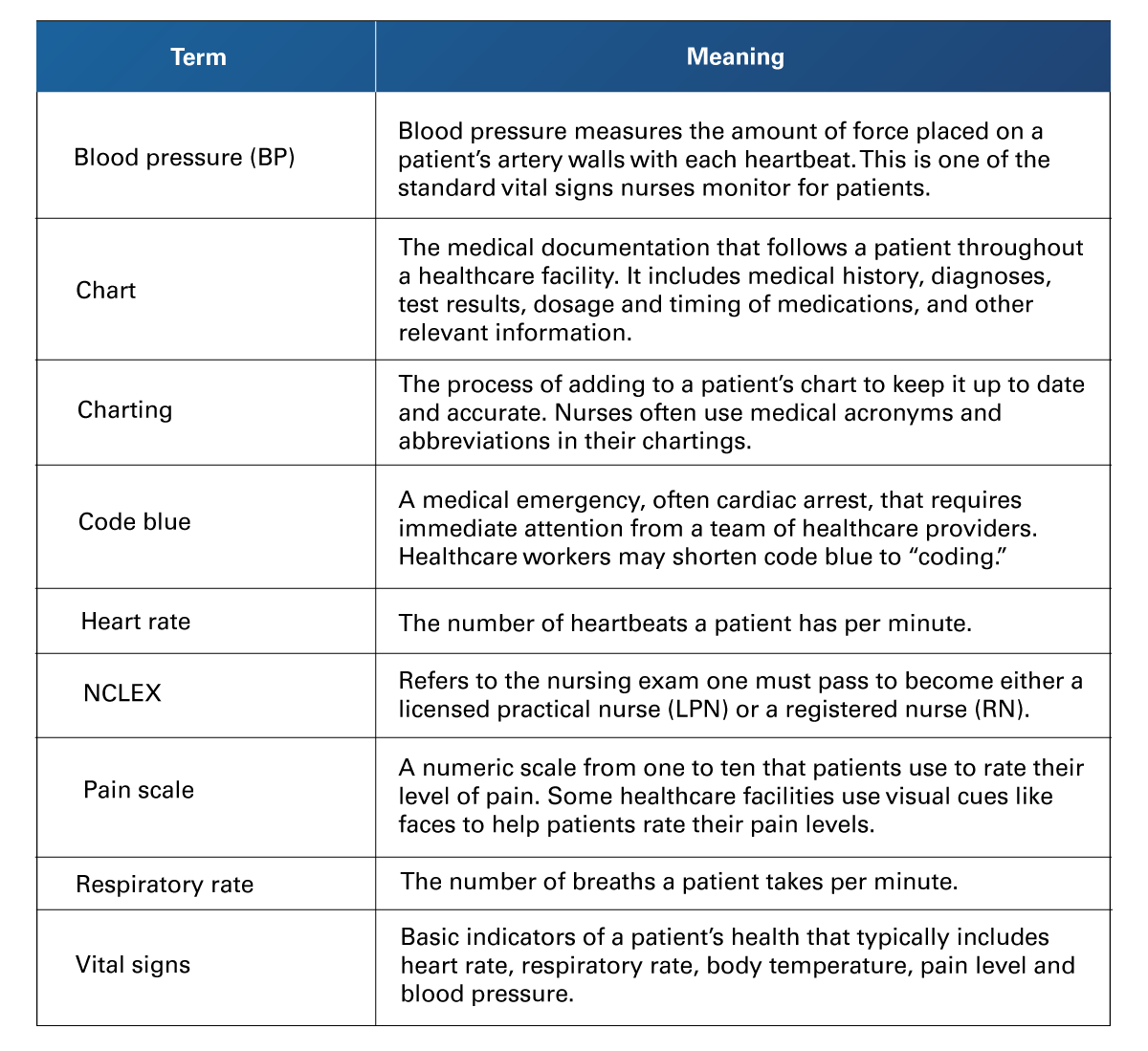 Retrieved from Brooks, A. (2021). Common nursing terms: A cheat sheet for new nurses. https://www.rasmussen.edu/degrees/nursing/blog/common-nursing-terms/
Retrieved from Brooks, A. (2021). Common nursing terms: A cheat sheet for new nurses. https://www.rasmussen.edu/degrees/nursing/blog/common-nursing-terms/
Table 3
Nursing Acronyms
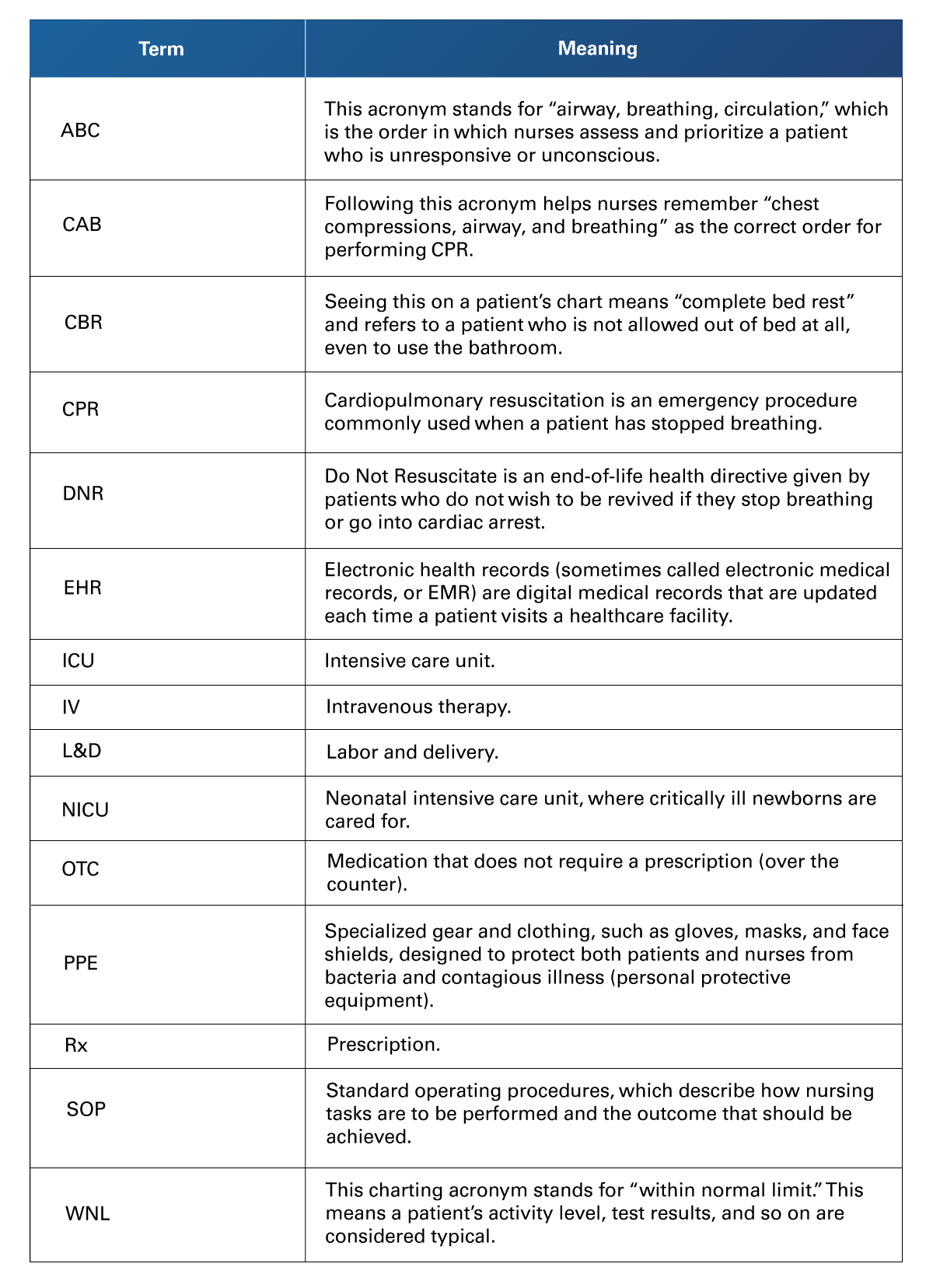 Retrieved from Brooks, A. (2021). Common nursing terms: A cheat sheet for new nurses. https://www.rasmussen.edu/degrees/nursing/blog/common-nursing-terms/
Retrieved from Brooks, A. (2021). Common nursing terms: A cheat sheet for new nurses. https://www.rasmussen.edu/degrees/nursing/blog/common-nursing-terms/
Table 4
Common Medical Test and Procedures
 Retrieved from Brooks, A. (2021). Common nursing terms: A cheat sheet for new nurses. https://www.rasmussen.edu/degrees/nursing/blog/common-nursing-terms/
Retrieved from Brooks, A. (2021). Common nursing terms: A cheat sheet for new nurses. https://www.rasmussen.edu/degrees/nursing/blog/common-nursing-terms/
Table 5
Health Care Business Terms
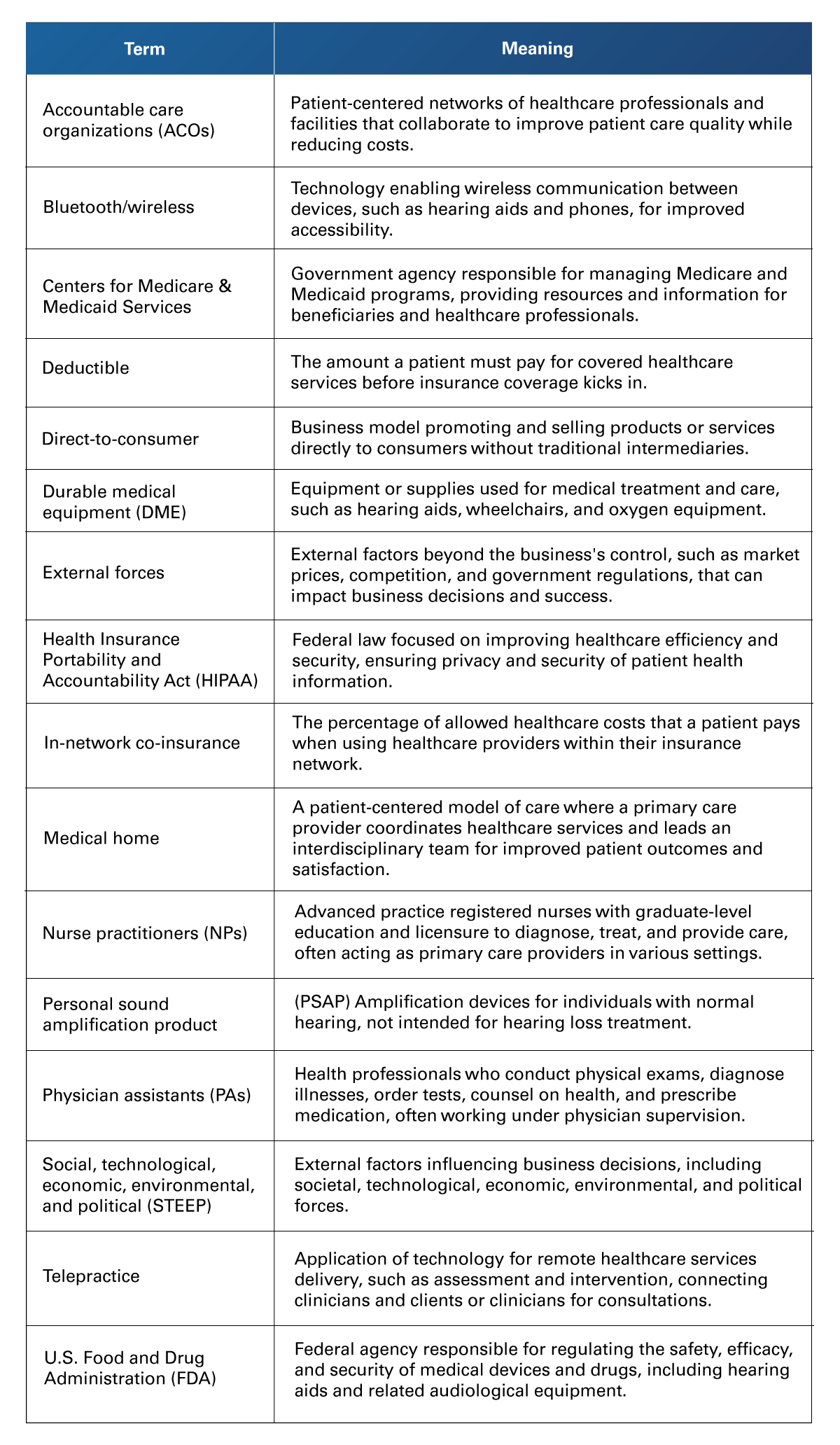 Retrieved from American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. (n.d.). Glossary of health care business terms. https://www.asha.org/aud/glossary-of-health-care-business-terms/
Retrieved from American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. (n.d.). Glossary of health care business terms. https://www.asha.org/aud/glossary-of-health-care-business-terms/
Table 6
Health Care Quality and Safety Terms
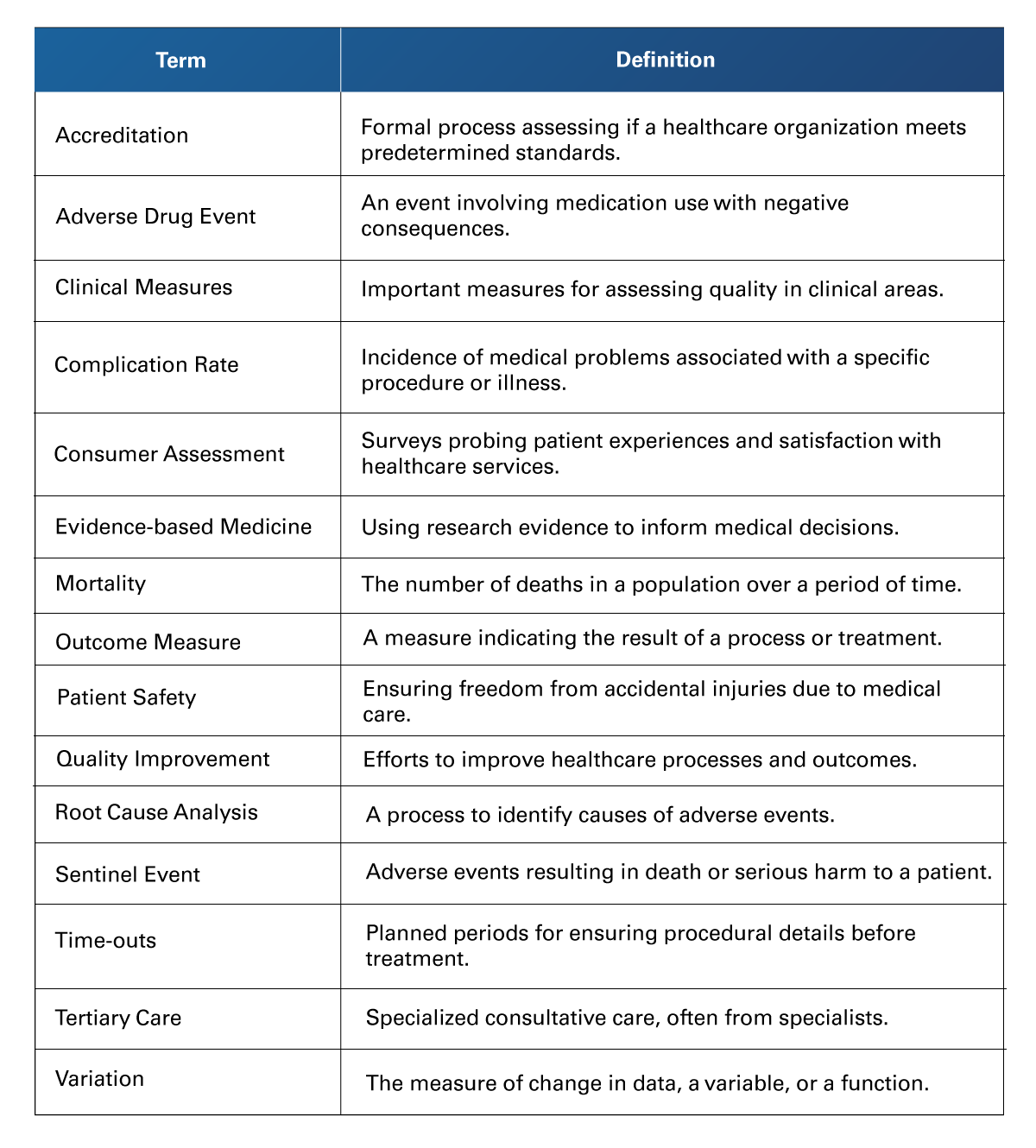 Retrieved from University of Rochester Medical Center. (n.d.). Glossary of terms. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/quality/glossary.aspx
Retrieved from University of Rochester Medical Center. (n.d.). Glossary of terms. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/quality/glossary.aspx
 In summary, throughout this learning experience, you have explored into the nursing process, which serves as a comprehensive scientific foundation for decision-making rooted in evidence-based practice. This approach emanates from a scientific perspective, aiding in effective clinical choices. Additionally, you've explored how nurses utilize medical terminology to facilitate communication. However, application of medical terminology extends beyond patient interactions, as it seamlessly integrates into healthcare management to enhance patient care standards and optimize outcomes.
In summary, throughout this learning experience, you have explored into the nursing process, which serves as a comprehensive scientific foundation for decision-making rooted in evidence-based practice. This approach emanates from a scientific perspective, aiding in effective clinical choices. Additionally, you've explored how nurses utilize medical terminology to facilitate communication. However, application of medical terminology extends beyond patient interactions, as it seamlessly integrates into healthcare management to enhance patient care standards and optimize outcomes.
In the context of our case scenario, Rosa, an 86-year-old woman, gets admitted and discharged from the hospital. Her patient journey is distinct, shaped by every interaction with the dedicated healthcare professionals attending to her. Each nurse provides care based on a careful synthesis of the nursing process, harmonizing it with the specific context of care delivery. Proficiency in medical terminology is essential, as precise communication stands as a cornerstone of effective and safe healthcare management provision. Moreover, it enhances the patient’s experience, making it more gratifying and fulfilling (Daly et al., 2005; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2018; Singh, 2016). This proficiency in communication aligns with the overarching goal of improving patient care quality and overall satisfaction.
In the United States of America, each state calls upon the Board of Nursing (BON) to determine the appropriate examination that indicates competence for granting a license to practice as a licensed nurse (NCSBN, n.d.). The NCLEX employs the nursing process, nursing context, and healthcare management terminology as its communication channel. Learning and memorizing medical terminology in English, and achieving proficiency to pass the NCLEX, leads the learner to obtain their licensure.
Remember that medical terminology is an ever-evolving field, making it essential to remain updated on new terms and advancements. For further assistance, it is advisable to consult reputable medical dictionaries, textbooks, or online resources. You can also explore the bibliography and resources included in this course. Wishing you the best of luck in your future nursing career.
- NCSBN. (n.d.). About U.S. Nursing Regulatory Bodies. https://ncsbn.org/nursing-regulation/about-nursing-regulatory-bodies.page
- Ackley, B. J., & Ladwig, G. B. (2010). Nursing diagnosis handbook: An evidence-based guide to planning care. Elsevier Health Sciences.
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. (n.d.). Glossary of health care business terms. https://www.asha.org/aud/glossary-of-health-care-business-terms/
- Brooks, A. (2021). Common nursing terms: A cheat sheet for new nurses. https://www.rasmussen.edu/degrees/nursing/blog/common-nursing-terms/
- Daly, J., Speedy, S., Jackson, D., Lambert, V., & Lambert, C. (2005). Professional nursing: Concepts, issues, and challenges. Springer Publishing Company.
- Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (2018). Lippincott visual nursing: A guide to clinical diseases, skills, and treatments (3rd ed.). Wolters Kluwer.
- Singh, N. R. (2016). NURSING: The Ultimate study guide (2nd ed.). Springer Publishing Company.
- University of Rochester Medical Center. (n.d.). Glossary of terms. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/quality/glossary.aspx
The following links do not belong to Tecmilenio University, when accessing to them, you must accept their terms and conditions.
Readings
- Betts, J. G., Young, K. A., Wise, J. A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Kruse, D. H., Karol, O., Johnson, J. E., Womble, M. & DeSaix, P. (2013). Anatomy and physiology. OpenStax. http://cnx.org/content/col11496/latest/
- Faubion, D. (n.d.). The 5 Nursing Process Steps – (Learn Each Step in Detail). https://www.nursingprocess.org/Nursing-Process-Steps.html
- Gaines, K. (2023). The ultimate guide to nursing diagnosis in 2023. https://nurse.org/resources/nursing-diagnosis-guide/#nanda-diagnosis
- Global RPH. (n.d.). Medical terminology - A thru Z.
- Medline Plus. (n.d.). Understanding medical words tutorial from the National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/medwords/medicalwords.html
- MERCK MANUAL. (n.d.). Pronunciations. https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/pronunciations#
- National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention. (n.d.). Dangerous abbreviations. http://www.nccmerp.org/dangerous-abbreviations
- Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical terminology for healthcare professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. Available from: https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
- Squires, A. (2011). The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and Mexican nursing. Health policy and planning, 26(2). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3040368/
- The Joint Commission. (2018). Official “Do Not Use” list. https://www.jointcommission.org/-/media/tjc/documents/resources/patient-safety-topics/patient-safety/do_not_use_list_9_14_18.pdf
- Toney, T. J., & Thayer, J. M. (2023). Nursing process. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499937/
La obra presentada es propiedad de ENSEÑANZA E INVESTIGACIÓN SUPERIOR A.C. (UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO), protegida por la Ley Federal de Derecho de Autor; la alteración o deformación de una obra, así como su reproducción, exhibición o ejecución pública sin el consentimiento de su autor y titular de los derechos correspondientes es constitutivo de un delito tipificado en la Ley Federal de Derechos de Autor, así como en las Leyes Internacionales de Derecho de Autor.
El uso de imágenes, fragmentos de videos, fragmentos de eventos culturales, programas y demás material que sea objeto de protección de los derechos de autor, es exclusivamente para fines educativos e informativos, y cualquier uso distinto como el lucro, reproducción, edición o modificación, será perseguido y sancionado por UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO.
Queda prohibido copiar, reproducir, distribuir, publicar, transmitir, difundir, o en cualquier modo explotar cualquier parte de esta obra sin la autorización previa por escrito de UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO. Sin embargo, usted podrá bajar material a su computadora personal para uso exclusivamente personal o educacional y no comercial limitado a una copia por página. No se podrá remover o alterar de la copia ninguna leyenda de Derechos de Autor o la que manifieste la autoría del material.