Psychosocial Integrity / Topic 4
Make sure to:
- Demonstrate knowledge of expected reactions to grief and loss.
- Provide care for clients experiencing grief and loss.
- Evaluate clients' responses to the care they receive during periods of grief and loss.
 Many people experience grief and loss, and life after such loss can be daunting. As nurses will undoubtedly encounter clients experiencing grief and loss, they should be prepared to assist them during the grieving process.
Many people experience grief and loss, and life after such loss can be daunting. As nurses will undoubtedly encounter clients experiencing grief and loss, they should be prepared to assist them during the grieving process.
In this learning experience, learners will gain knowledge and insight into expected reactions to grief and loss, in addition to learning how to care for clients who are experiencing grief and loss and how to evaluate their responses to care.
4.1 Expected Reactions to Grief and Loss
 Nurses need to be aware of the expected reactions to grief and loss to assist their clients in coping during the grieving process. Their competence increases with knowledge about the definition of grief, as well as the classification and impact of grief and loss.
Nurses need to be aware of the expected reactions to grief and loss to assist their clients in coping during the grieving process. Their competence increases with knowledge about the definition of grief, as well as the classification and impact of grief and loss.
According to Burke (2023), the National North American Nursing Diagnosis Association International defines grief as a normal, complex process that includes emotional, physical, spiritual, social and intellectual responses and behaviors by which individuals, families, and communities incorporate a loss into their daily lives. Additionally, Burke (2023) describes grief as a normal response to loss, which can be classified as:
- Normal Grief: The client employs healthy coping and adaptive strategies.
- Complicated Dysfunctional Grief: The duration of grief extends beyond the expected timeframe.
- Anticipatory Grief: Experiencing grief before the loss occurs.
- Disenfranchised Grief: Grieving a loss that is due to a socially unacceptable event, such as drug overdose.
- Grief Resulting of a Public Tragedy: Grieving due to a natural or man-made disaster, such as a major flood or terrorism at the World Center.
It is important to remember that all losses impact the individuals who experience them, and these losses can be intrapersonal or extrapersonal (Burke, 2023).
- Intrapersonal Losses:
- Loss of self or body image.
- Extrapersonal Losses:
- Loss of:
- A pet
- A friendship
- Life savings
- Death of a loved one, including:
- A child
- A spouse
According to Burke (2023) losses can be classified as:
- Actual loss, where the loss has actually occurred.
- Perceived loss, which is based on the client's perception rather than reality and has not actually occurred.
- Situational loss, such as the loss of a loved one.
- Developmental or maturational loss, and necessary loss, in developmental loss, the client loses aspects like their youth, while in necessary loss, the loss is considered a normal and expected part of the life span.
According to Burke (2023), during grieving process, nurses can anticipate that their clients may exhibit the following characteristics:
- Anger
- Despair
- Detachment
- Distress
- Guilt
- Impaired sleep
- Pain
- Personal growth
- Suffering
Furthermore, according to Burke (2023), grief and loss can lead to a range of physiological and psychological responses, including altered immune responses, distress, anger, sleep disturbances, blame, withdrawal, pain, panic, suffering and alterations with neuroendocrine functioning.
4.2 Care of Clients Experiencing Grief and Loss

Nurses must follow the policies and procedures of their healthcare facilities when creating nursing care plans for clients experiencing grief and loss. This includes supporting clients who are going through anticipatory grief and providing resources to help them cope with their loss (Burke, 2023). It is also essential for nurses to document and report any abnormal findings and adhere to the follow-up instructions given by healthcare providers.
In planning care for clients dealing with grief and loss, nurses should be well-versed in the theoretical sequential concepts/reactions typically exhibited by such clients. They should also educate their clients about these expected reactions, as detailed in Table 1 (Burke, 2023).
Table 1
Theories for Grief and Loss and The Sequences of Their Concepts/Reactions.
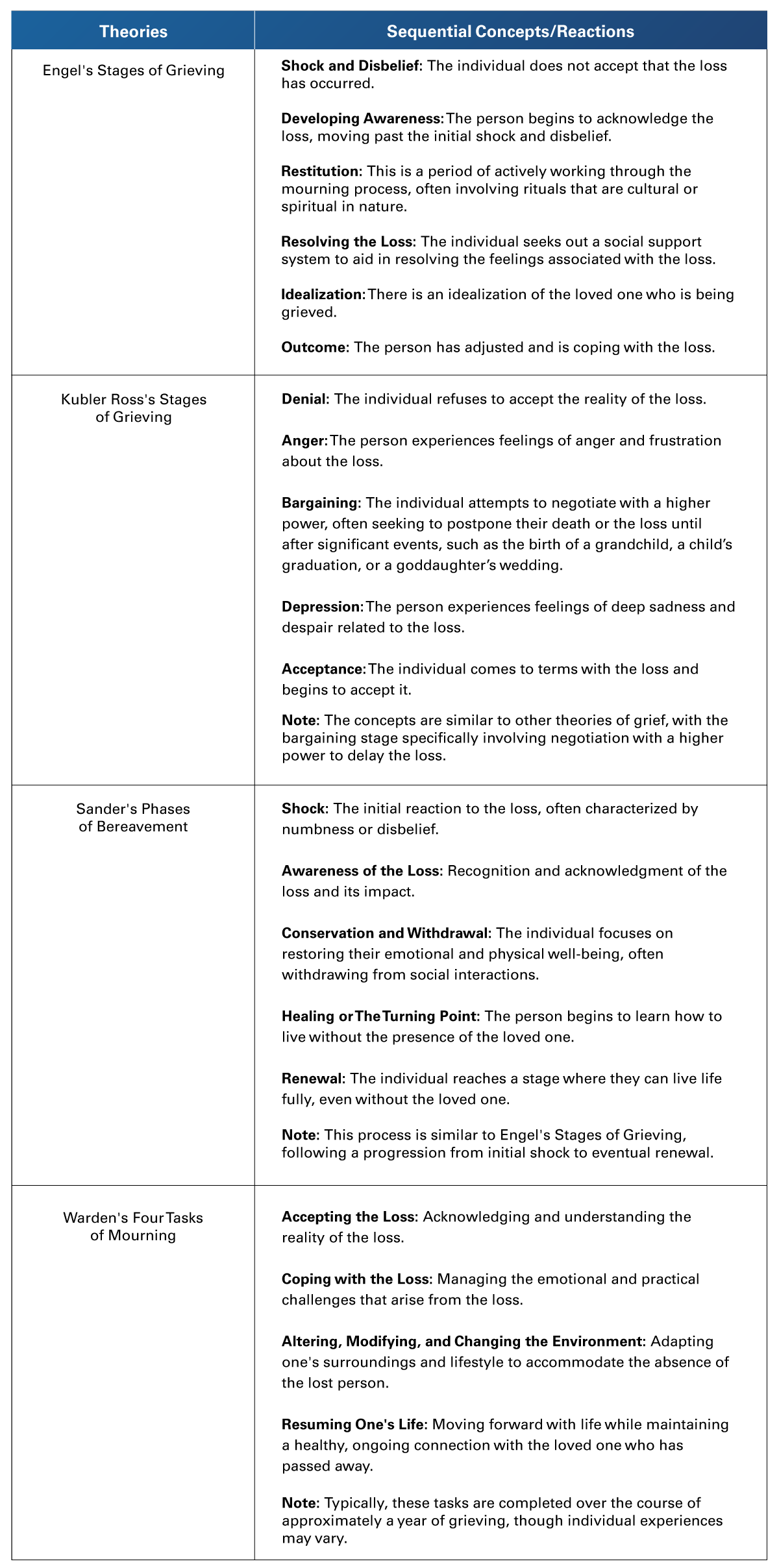 Adapted from Burke, A. (2023). Grief and Loss: NCLEX-RN. https://www.registerednursing.org/nclex/grief-loss/
Adapted from Burke, A. (2023). Grief and Loss: NCLEX-RN. https://www.registerednursing.org/nclex/grief-loss/
Promoting normal grieving and preventing complicated grieving is essential (Burke, 2023) This can be accomplished by establishing a trusting relationship with clients who are grieving, allowing them to freely express their feeling, and offering a nonjudgmental space where they can learn coping skills (Burke, 2023). Referrals to community resources such as support and peer groups or counseling can be beneficial, and family support can also be instrumental. In addition, nurses must recognize that the grieving process varies from client-to-client and is influenced by factors such as:
- Socioeconomic status.
- The intensity and significance of the loss.
- Religious, spiritual and cultural backgrounds.
- The stage of growth and development, which influences the client's understanding of death.
- Support systems, including relationships and social groups.
3. Evaluate Clients' Responses to Care
 Nurses should continuously evaluate their clients' response to treatment and adjust their care plans as needed (Burke, 2023). It is important to evaluate:
Nurses should continuously evaluate their clients' response to treatment and adjust their care plans as needed (Burke, 2023). It is important to evaluate:
- The specific stage or phase each client is in within the grieving process and whether they are progressing through the expected sequence of reactions (Kaplan Nursing, 2023).
- The extent the client has resumed social activities (Kaplan Nursing, 2023).
Additionally, Burke (2023) recommends that nurses evaluate clients for the following desired outcomes:
- The absence of complicated grieving.
- The verbalization and expression of authentic feelings.
- The utilization of support systems.
- The identification of personal strengths and areas that require improvement.
- The use of effective coping mechanisms.
- Discussions about the meaning and impact of their loss.
 Upon completing this learning experience, learners will have gained the necessary knowledge to assess, care for, and evaluate clients who are experiencing grief and loss. The main goals are to prepare learners for successful performance on the NCLEX examination and to enhance their professional competency in handling grief and loss situations in the workplace.
Upon completing this learning experience, learners will have gained the necessary knowledge to assess, care for, and evaluate clients who are experiencing grief and loss. The main goals are to prepare learners for successful performance on the NCLEX examination and to enhance their professional competency in handling grief and loss situations in the workplace.
Review the following resources with the aim of deepening understanding and insights into the processes of grief and loss.
- Burke, A. (2023, October 1). Grief and Loss: NCLEX-RN. https://www.registerednursing.org/nclex/grief-loss/
- Kaplan Nursing. (2023). NCLEX-RN Content Review Guide: Preparation for the NCLEX-RN Examination (9th ed.). Kaplan Test Prep.
The following links do not belong to Tecmilenio University, when accessing to them, you must accept their terms and conditions.
Readings
- American Psychological Association. (2020, January 1). Grief: Coping with the Loss of Your Loved One. https://www.apa.org/topics/families/grief
Videos
- Psych2Go. (2019, December 19). How to Deal with Loss or Grief of Loved Ones [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/Jl7axuIeVxI
La obra presentada es propiedad de ENSEÑANZA E INVESTIGACIÓN SUPERIOR A.C. (UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO), protegida por la Ley Federal de Derecho de Autor; la alteración o deformación de una obra, así como su reproducción, exhibición o ejecución pública sin el consentimiento de su autor y titular de los derechos correspondientes es constitutivo de un delito tipificado en la Ley Federal de Derechos de Autor, así como en las Leyes Internacionales de Derecho de Autor.
El uso de imágenes, fragmentos de videos, fragmentos de eventos culturales, programas y demás material que sea objeto de protección de los derechos de autor, es exclusivamente para fines educativos e informativos, y cualquier uso distinto como el lucro, reproducción, edición o modificación, será perseguido y sancionado por UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO.
Queda prohibido copiar, reproducir, distribuir, publicar, transmitir, difundir, o en cualquier modo explotar cualquier parte de esta obra sin la autorización previa por escrito de UNIVERSIDAD TECMILENIO. Sin embargo, usted podrá bajar material a su computadora personal para uso exclusivamente personal o educacional y no comercial limitado a una copia por página. No se podrá remover o alterar de la copia ninguna leyenda de Derechos de Autor o la que manifieste la autoría del material.